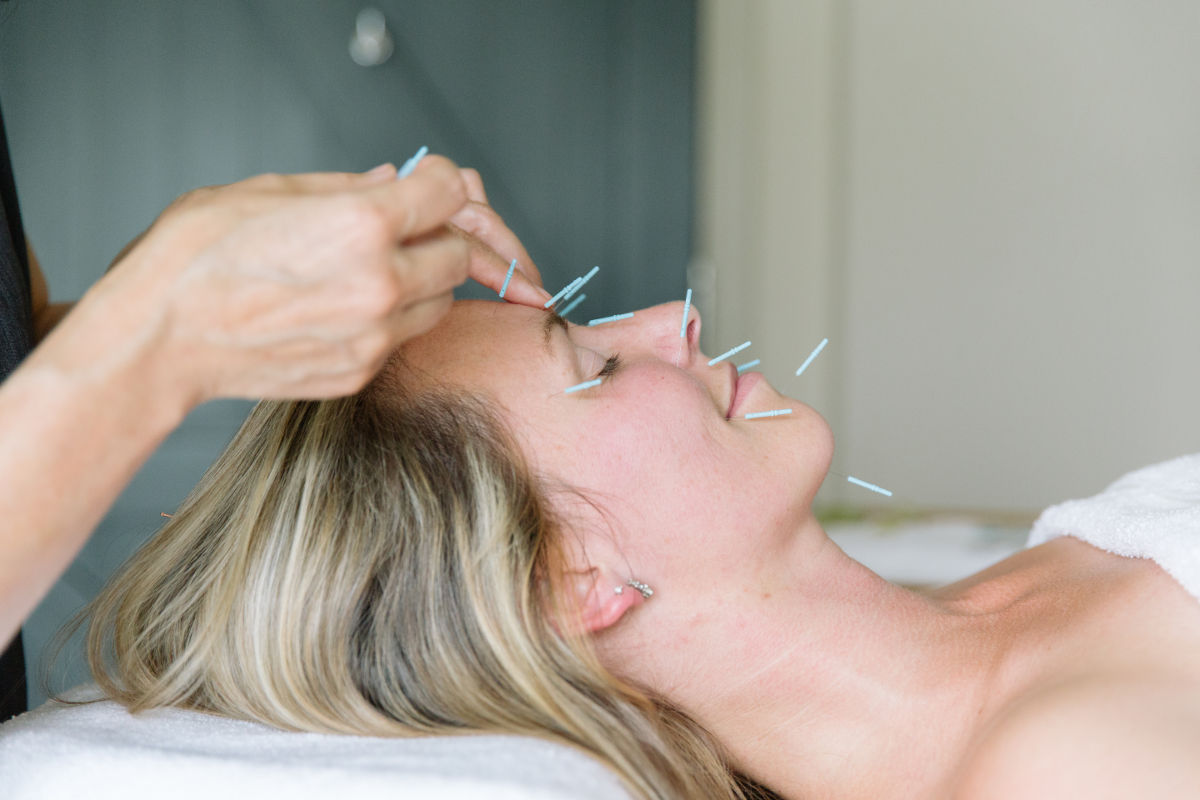
Acupuncture for Facial & Cosmetic Conditions.
Conditions affecting the face can be greatly distressing and impact the quality of life of those affected. Facial paralysis and Bell's palsy, trigeminal neuralgia and temporomandibular disorders causing jaw pain and tension are common conditions which can be treated by acupuncture.
While injectables, lasers, and surgical interventions have traditionally been used to reverse the changes associated with facial ageing, therapies such as facial acupuncture are now being studied for facial rejuvenation. Reviews of data from clinical studies suggest that facial acupuncture has the potential to improve skin elasticity, wrinkle length, muscle thickness, and pigment changes associated with ageing.
What does the research say?
The following insights are obtained from systematic reviews and analysis of clinical trials investigating the efficacy of Chinese medicine and acupuncture for facial & cosmetic conditions.
2022 Journal of Complementary and Alternative Medical Research
Acupuncture has shown to be potentially beneficial as an alternate or adjunct therapy for patients with Bell's palsy following recovery from COVID-19.
In the methodology utilized for this research, an extensive literature search was carried out by two independent investigators. They used multiple sources including PubMed, MEDLINE, Google scholar, LILACS, and the Cochrane Register of Controlled Trials, from the year 2000 up until 2021. They used the keywords: Bell’s Palsy, covid-19, acupuncture, Mucormycosis, vaccine, and steroids. Selected articles were only those published in English and included full-text. The studies included in the review were all randomized controlled trials which compared acupuncture intervention's clinical effects (used alone or add on) with no treatment.
In terms of results, although the methodological quality of most studies was considered generally low, six randomized controlled trials were found to be satisfactory and included in the study. According to the results across these studies, the groups who received acupuncture treatment reported improved outcomes compared to their baseline or control groups. This was evident as no negative side effects were reported. The review therefore indicates that acupuncture could play a beneficial role in treating patients with Bell's palsy post-recovery from COVID-19, particularly those at risk of mucormycosis and other severe health complications.
Can Acupuncture be an Adjunct Therapy for Bell’s palsy Post COVID-19? Acupuncture for Bell’s Palsy: A Review Yepthomi T, Somanadhapai S
2022 Complementary Therapies in Medicine
Auricular acupuncture was found to improve physical and emotional aspects in patients with temporomandibular disorders, with similar results to occlusal splint treatment.
In the study, patients suffering from temporomandibular disorders were allocated into three groups - those who received auricular acupuncture (AA), those treated with occlusal splints (OS), and a sham group. The patients were evaluated and monitored over an eight-week period using axes I and II of the RDC-TMD according to CONSORT guidelines.
The findings revealed significant improvements in both the emotional aspects and physical aspects amidst the auricular acupuncture group and occlusal splint group. The sham group showed no improvements in the emotional aspect and only a few in the physical aspect. The comparison between the auricular acupuncture group and the occlusal splint group revealed similar number of variables with improved outcomes, indicating that the auricular acupuncture treatment was as effective as the occlusal splint treatment. On the other hand, the sham group presented a significant difference when compared to the other groups. These results strongly suggest the potential of auricular acupuncture as a treatment option for temporomandibular disorders.
Auricular acupuncture in TMD — A sham-controlled, randomized, clinical trial Aroca JP, Cardoso PMF, Favarão J, Zanini MM, Camilotti V, Busato MCA, Mendonça MJ, Alanis LRA
2020 Cosmetics
Both facial acupuncture and facial exercises have the potential to improve the skin laxity, wrinkle length, muscle thickness, and pigmentary changes associated with aging.
While injectables, lasers, and surgical interventions have traditionally been used to reverse the changes associated with facial aging, other alternative therapies such as facial acupuncture and facial exercises are now being studied for facial rejuvenation. In this paper, we both summarize the concepts of facial acupuncture and facial exercises, and review seven studies that evaluate the efficacy of these modalities. Data from these studies suggest that both facial acupuncture and facial exercises have the potential to improve the skin laxity, wrinkle length, muscle thickness, and pigmentary changes associated with aging. Patients frequently reported improvement and experienced very few side effects. However, further research is necessary before these modalities are widely accepted as effective by the medical community, though the results of these studies may ultimately make providers less hesitant when patients seek out these services.
Non-Traditional and Non-Invasive Approaches in Facial Rejuvenation: A Brief Review M. Smith, A. Ferris, T. K. Nahar, V. Sharma, M.
2020 Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment
Acupuncture is associated with a reduction in the risk of depression during long-term follow-up in patients with trigeminal neuralgia.
In total, 776 patients with newly diagnosed trigeminal neuralgia in each cohort with similar baseline characteristics were enrolled in the study. The acupuncture cohort had a reduced risk of depression compared to the non-acupuncture cohort. Kaplan–Meier analysis also revealed that the cumulative incidence of depression was significantly lower in the acupuncture cohort during the 13-year follow-up period. In particular, the beneficial effect of acupuncture was a decrease in the risk of depression among TN patients aged 50– 69 years who had also used carbamazepine.
Long-Term Beneficial Effects of Acupuncture with Reduced Risk of Depression Development Following Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study Liao CC, Lin CL, Liao KR, Li JM
2020 Revista Internacional de Acupuntura
Acupuncture therapy seems to decrease frequency and intensity of trigeminal neuralgia pain episodes, alone or in combination with gold standard medications.
Among the six studies selected, most were randomized controlled clinical trials, developed in China. Only one study performed a retrospective cross-sectional. To assess pain, most used the VAS scale. There were very similar methods concerning points selection and treatment protocols. All studies found a significant decrease in pain frequency or intensity, disregarding the type of acupuncture applied.
Acupuncture therapy in trigeminal neuralgia: An integrative literature review Aquino I, Nascimento M, Aquino T, Kosminsky M
2020 Journal of Oral Rehabilitation
Acupuncture, regardless of whether on specific or non-specific points, substantially decreases non-chronic pain in patients suffering from Temporomandibular Disorders.
In this double-blinded, single-centre, randomized controlled trial, 49 patients with non-chronic painful Temporomandibular Disorders were divided into two groups. Group A received acupuncture on specific points, while Group B had acupuncture on non-specific points. Subjects were examined, treated weekly with acupuncture for a month by a dentist, and reexamined five weeks after the initial examination by an examiner unaware of the study groups. The main criteria for assessment was characteristic pain intensity, with other factors considered including mouth opening ability, patients' expectations regarding treatment, mood, and oral health-related quality of life.
The results indicated that neither age nor characteristic pain intensity significantly differed between the two groups. However, characteristic pain intensity was notably lower five weeks post initial examination for both groups. A perceived increase in mouth-opening capacity, enhanced oral health-related quality of life, and a substantial reduction in mood disorder symptoms were encountered, with all patients holding positive views towards acupuncture therapy. The findings determined that the reduction of non-chronic pain from Temporomandibular Disorders through acupuncture cannot be credited to the selection of specific points alone.
Comparison of acupuncture on specific and nonâ€specific points for the treatment of painful temporomandibular disorders: A randomised controlled trial Åžen S, Orhan G, Sertel S, Schmitter M, Schindler HJ, Lux CJ, Giannakopoulos NN
2019 Acupuncture in Medicine
Acupuncture might be effective at reducing itch intensity and may be more effective than conventional medicine at reducing eczema area and severity index (EASI) and improving the global symptoms of atopic eczema.
Acupuncture might be an effective treatment capable of reducing itch intensity, and may be more effective than conventional medicine at reducing EASI and improving global symptoms for patients with AE. Acupuncture is a safe treatment for patients with AE, but the available data are too few to suggest that acupuncture alone is effective at improving quality of life and recurrence rate. More high-quality trials with larger sample sizes are needed to confirm the effects of acupuncture on AE.
The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for patients with atopic eczema: a systematic review and meta-analysis Jiao R, Yang Z, Wang Y, Zhou J, Zeng Y, Liu Z
2018 Journal of Cosmetic Medicine
The safety of cosmetic acupuncture appears tolerable, however, well-designed high-quality studies, are needed to determine its effects on facial cosmetic conditions.
Our systematic review of 2 RCTs and 5 prospective, single- armed studies demonstrated that there are a few trials with high-quality evidence regarding cosmetic acupuncture for facial cosmetic conditions. The safety of cosmetic acupuncture appears tolerable; however, well-designed high-quality studies, such as sham-controlled studies with standardized cosmetic acupuncture interventions, are needed to determine its effects on facial cosmetic conditions.
Acupuncture for cosmetic use: a systematic review of prospective studies Byung-Cheul Shin & Kyeong-Tae Lim
2017 Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine
In oral care, acupuncture can be a supplement to conventional treatments in temporomandibular disorders, facial pain, pain management, Sjoegrens syndrome, and in phobias and anxiety.
Acupuncture aims to treat a range of medical and dental ailments, though is most commonly used for pain relief. This article reviews about the various possible roles of acupuncture in clinical dental practice. Acupuncture has potential in supplementing conventional treatment procedures by its diverse applicability outreach. Role of acupuncture in dental practice has been well supported by clinical trials. Its role in alleviating facial pain, pre-operative and post-operative dental pain has led to its widespread application.
Acupuncture (é‡ç¸ ZhÄ“n JiÇ”) – An Emerging Adjunct in Routine Oral Care Gupta, D., Dalai, D., Swapnadeep, Mehta, P.D., Indra, B., Rastogi, S., Jain, A., Chaturvedi, M., Sharma, S., Singh, S., Gill, S., Singh, N., & Gupta, R. (2014). Acupuncture (é‡ç¸ ZhÄ“n JiÇ”) – An Emerging Adjunct in Routine Oral Care. Journal of Tradi
2017 Medicine
Acupuncture therapy is effective in reducing the degree of pain in patients with temporomandibular disorders, especially those with myofascial pain symptoms.
This study compared the clinical effectiveness of acupuncture therapy in TMD patients through the meta-analysis of published results. Our results indicate that acupuncture therapy penetrating the skin has greater effectiveness and reduces the pain degree to a greater extent, especially myofascial pain symptoms, compared with both sham nonpenetrating acupuncture and sham laser therapy.
Acupuncture therapy in the management of the clinical outcomes for temporomandibular disorders Wu, Jun-Yi MD; Zhang, Chao MD; Xu, Yang-Peng MM; Yu, Ya-Yu MD; Peng, Le PhD; Leng, Wei-Dong PhD; Niu, Yu-Ming PhD; Deng, Mo-Hong PhD
2017 Medicine
Acupuncture therapy is effective in reducing the degree of pain in patients with temporomandibular disorders, especially those with myofascial pain symptoms.
This study compared the clinical effectiveness of acupuncture therapy in TMD patients through the meta-analysis of published results. Our results indicate that acupuncture therapy penetrating the skin has greater effectiveness and reduces the pain degree to a greater extent, especially myofascial pain symptoms, compared with both sham nonpenetrating acupuncture and sham laser therapy.
Acupuncture therapy in the management of the clinical outcomes for temporomandibular disorders Wu, Jun-Yi MD; Zhang, Chao MD; Xu, Yang-Peng MM; Yu, Ya-Yu MD; Peng, Le PhD; Leng, Wei-Dong PhD; Niu, Yu-Ming PhD; Deng, Mo-Hong PhD
2015 Neurology
The majority of trials demonstrate a positive effect of acupuncture over control condition in the treatment of neuropathy.
The majority of RCTs reviewed showed clear benefit for acupuncture over control in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy, Bell’s palsy and carpal tunnel syndrome. Acupuncture is probably effective in the treatment of HIV-related neuropathy and there is insufficient evidence for its benefits in idiopathic neuropathy. Meta-analyses of all diabetic neuropathy and bell’s palsy data using a summary estimate random effects model showed combined Odds Ratio (OR) of 4.23, p<0.001 favoring acupuncture over control for pain outcomes. The majority of trials demonstrate a positive effect of acupuncture over control condition in the treatment of neuropathy. Further more rigorously designed studies are needed to better characterize this effect.
Effects of Acupuncture on Neuropathic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Alexandra Dimitrova, Charles Murchison, Barry Oken
2015 PLOS One
Acupuncture proves to be a promising alternative therapy for treating Bell's palsy, despite some controversy surrounding its use.
To assess the effectiveness of acupuncture in treating Bell’s palsy, a systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted using data from PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, without any language restrictions being imposed. Fourteen randomized controlled trials that compared acupuncture with other therapies for the treatment of Bell's palsy in adults and children were included. The participant pool for these trials comprised 1541 individuals.
In the results, acupuncture showed a significant positive correlation with higher effective response rates for Bell's palsy. However, a notable variance was observed among the different studies. Furthermore, a lack of complete data made it impossible to evaluate the incidence of complications. Despite this limitation, acupuncture emerged as an effective therapy for Bell's palsy. It must be emphasized that the results should be interpreted with caution due to concerns about the poor quality and heterogeneity of the included studies.
Efficacy of Acupuncture for Bell’s Palsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Li, P., Qiu, T., & Qin, C.
2010 The Clinical Journal of Pain
Acupuncture is a reasonable adjunctive treatment for producing a short-term analgesic effect in patients with painful temporomandibular disorder symptoms.
The results of this meta-analysis suggest that acupuncture is a reasonable adjunctive treatment for producing a short-term analgesic effect in patients with painful TMD symptoms. Although the results described are positive, the relevance of these results was limited by the fact that substantial bias was present. These findings must be confirmed by future RCTs that improve the methodologic deficiencies of the studies evaluated in this meta-analysis.
Acupuncture in the treatment of pain in temporomandibular disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials La Touche R, Goddard G, De-la-Hoz JL, Wang K, Paris-Alemany A, Angulo-DÃaz-Parreño S, Mesa J, Hernández M
2010 Evidence-Based Dentistry
There is limited evidence that acupuncture is more effective than sham acupuncture in alleviating pain and masseter muscle tenderness in temporomandibular disorders.
Seven RCTs (including 141 patients) met our inclusion criteria. Six studies comparatively tested needle acupuncture against penetrating sham acupuncture, non-penetrating sham acupuncture or sham laser acupuncture, whilst the remaining study tested laser acupuncture against sham laser acupuncture. Five studies were considered to be at low risk of bias. Outcomes were reported for pain intensity, facial pain, muscle tenderness and mouth opening.
Limited evidence that acupuncture is effective for treating temporomandibular disorders Jens C Türp
2010 Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies
Chinese acupuncture is safe and can be efficient in alleviating pain in patients suffering from temporomandibular disorder without clear joint pathology.
The results of this study showed that Chinese acupuncture was safe as administered here and was efficient in alleviating pain in patients suffering from temporomandibular disorder not caused by an osseous source. In approximately 90% of these patients, a statistically significant pain alleviation was observed, with the pain completely gone in most patients.
Acupuncture for treating temporomandibular disorder: retrospective study on safety and efficacy Noiman M, Garty A, Maimon Y, Miller U, Lev-Ari S.
2010 Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies
Chinese acupuncture is safe and can be efficient in alleviating pain in patients suffering from temporomandibular disorder without clear joint pathology.
The results of this study showed that Chinese acupuncture was safe as administered here and was efficient in alleviating pain in patients suffering from temporomandibular disorder not caused by an osseous source. In approximately 90% of these patients, a statistically significant pain alleviation was observed, with the pain completely gone in most patients.
Acupuncture for treating temporomandibular disorder: retrospective study on safety and efficacy Noiman M, Garty A, Maimon Y, Miller U, Lev-Ari S.
Consult with our practitioners for personalised care and advice.
Although well-conducted clinical research can help members of the public to make better-informed decisions about their healthcare, we cannot claim that any particular treatment may be effective for any individual person.
When you consult with our Chinese medicine practitioners, you'll receive personalised advice and treatment based on your symptoms and Chinese medicine diagnosis.
Scientific References
Browse our collection of scientific clinical research on acupuncture for facial & cosmetic conditions.
It includes recent and reputable papers published by peer-reviewed journals within the last 10 years.

2022, Jul 13
Can Acupuncture be an Adjunct Therapy for Bell’s palsy Post COVID-19? Acupuncture for Bell’s Palsy: A Review
Journal of Complementary and Alternative Medical Research
Our review suggest that Acupuncture can be an adjunct or a good alternate therapy for patients with Bell’s palsy post recovery of COVID-19 infection and especially those with the risk of predisposed factor for mucormycosis and other severe health complication.
Yepthomi T, Somanadhapai S Full Article

2022, Aug
Auricular acupuncture in TMD — A sham-controlled, randomized, clinical trial
Complementary Therapies in Medicine
In conclusion, this study demonstrated that auricular acupuncture (AA) applied at a specific temporomandibular joint (TMJ) ear point was able to bring about improvements in patients with temporomandibular disorders (TMDs), with outcomes similar to those in patients treated with an occlusal splints (OS).
Aroca JP, Cardoso PMF, Favarão J, Zanini MM, Camilotti V, Busato MCA, Mendonça MJ, Alanis LRA Full Article

2020, Feb 12
Non-Traditional and Non-Invasive Approaches in Facial Rejuvenation: A Brief Review
Cosmetics
Data from these studies suggest that both facial acupuncture and facial exercises have the potential to improve the skin laxity, wrinkle length, muscle thickness, and pigmentary changes associated with aging. Patients frequently reported improvement and experienced very few side effects. However, further research is necessary before these modalities are widely accepted as effective by the medical community, though the results of these studies may ultimately make providers less hesitant when patients seek out these services.
M. Smith, A. Ferris, T. K. Nahar, V. Sharma, M. Full Article

2020, Dec
Long-Term Beneficial Effects of Acupuncture with Reduced Risk of Depression Development Following Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment
The systematic review and meta-analysis also concluded that the therapeutic efficacy of acupuncture is highly effective alone and combined with antidepressant medication.
Liao CC, Lin CL, Liao KR, Li JM Full Article

2020, Jul
Acupuncture therapy in trigeminal neuralgia: An integrative literature review
Revista Internacional de Acupuntura
This literature review indicated the decrease frequency and intensity of TN pain episodes in acupuncture patients.
Aquino I, Nascimento M, Aquino T, Kosminsky M Full Article

2020, Mar 09
Comparison of acupuncture on specific and nonâ€specific points for the treatment of painful temporomandibular disorders: A randomised controlled trial
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation
Acupuncture on both specific and non-specific points reduces the non-dysfunctional pain of temporomandibular disorder (TMD). patients. The effect of acupuncture on painful TMD cannot be attributed to the specific point selection.
Åžen S, Orhan G, Sertel S, Schmitter M, Schindler HJ, Lux CJ, Giannakopoulos NN Full Article

2019, Sep 09
The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for patients with atopic eczema: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Acupuncture in Medicine British Medical Acupuncture Society
Acupuncture is effective in reducing itch intensity and may be more beneficial than conventional medicine at reducing eczema symptoms. This study assessed the effectiveness and showed positive results from randomised controlled trials.
Jiao R, Yang Z, Wang Y, Zhou J, Zeng Y, Liu Z Full Article

2018, Dec 31
Acupuncture for cosmetic use: a systematic review of prospective studies
Journal of Cosmetic Medicine Korean Society of Korean Cosmetic Surgery and Medicine
This systematic review suggests that a few trials regarding acupuncture for cosmetic use have incorporated rigorous designs. Although the studies reported generally positive results with tolerable safety, the methodology of the trials should be updated in a rigorous manner, including the use of randomized, sham-controlled studies with standardized interventions, in order to provide sufficient evidence regarding the effects of cosmetic acupuncture.
Byung-Cheul Shin & Kyeong-Tae Lim Full Article

2017, Dec
Acupuncture (é‡ç¸ ZhÄ“n JiÇ”) – An Emerging Adjunct in Routine Oral Care
Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan
This article highlights the efficacy of acupuncture in reducing dental pain (eg. TMJ.facial paralysis) and lower risk of oral diseases.
Gupta, D., Dalai, D., Swapnadeep, Mehta, P.D., Indra, B., Rastogi, S., Jain, A., Chaturvedi, M., Sharma, S., Singh, S., Gill, S., Singh, N., & Gupta, R. (2014). Acupuncture (é‡ç¸ ZhÄ“n JiÇ”) – An Emerging Adjunct in Routine Oral Care. Journal of Tradi Full Article

2017, Mar
Acupuncture therapy in the management of the clinical outcomes for temporomandibular disorders
Medicine
The result of this article indicate that acupuncture is effective in reducing the degree of pain in patients with TMD, especially those with myofascial pain symptoms
Wu, Jun-Yi MD; Zhang, Chao MD; Xu, Yang-Peng MM; Yu, Ya-Yu MD; Peng, Le PhD; Leng, Wei-Dong PhD; Niu, Yu-Ming PhD; Deng, Mo-Hong PhD Full Article

2015, May 8
Effects of Acupuncture on Neuropathic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Neurology American Academy of Neurology
The majority of trials demonstrate a positive effect of acupuncture over control condition in the treatment of neuropathy. Further more rigorously designed studies are needed to better characterize this effect.
Alexandra Dimitrova, Charles Murchison, Barry Oken Full Article

2015, May 14
Efficacy of Acupuncture for Bell’s Palsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
PLOS One Public Library of Science
This review suggests that acupuncture may be an effective therapy for Bell’s palsy compared to drug therapy, but there was insufficient evidence to support the efficacy and safety of acupuncture.
Li, P., Qiu, T., & Qin, C. Full Article

2010, Jul
Acupuncture in the treatment of pain in temporomandibular disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
The Clinical Journal of Pain
The results of this meta-analysis suggest that acupuncture is a reasonable adjunctive treatment for producing a short-term analgesic effect in patients with painful TMD symptoms. Although the results described are positive, the relevance of these results was limited by the fact that substantial bias was present. These findings must be confirmed by future RCTs that improve the methodologic deficiencies of the studies evaluated in this meta-analysis.
La Touche R, Goddard G, De-la-Hoz JL, Wang K, Paris-Alemany A, Angulo-DÃaz-Parreño S, Mesa J, Hernández M Full Article

2010, Oct 7
Limited evidence that acupuncture is effective for treating temporomandibular disorders
Evidence-Based Dentistry British Dental Association
This systematic review highlighted that acupuncture is effective in alleviating pain and masseter muscle tenderness in TMD.
Jens C Türp Full Article

2010, Dec
Acupuncture for treating temporomandibular disorder: retrospective study on safety and efficacy
Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies Medical Association of Pharmacopuncture Institute
This article not just highlight the importance of acupuncture in relieving pain for TMJ disorders. It also showcase how acupuncture reduces stress and sleep quality, factors that have been demonstrated as risk factors for TMD and pain in general.
Noiman M, Garty A, Maimon Y, Miller U, Lev-Ari S. Full Article
“It is by virtue of the twelve channels that human life exists, that disease arises, that human beings can be treated and illness cured. The twelve channels are where beginners start and masters end.” The Classic of Acupuncture
Circa 1st Century BCE














