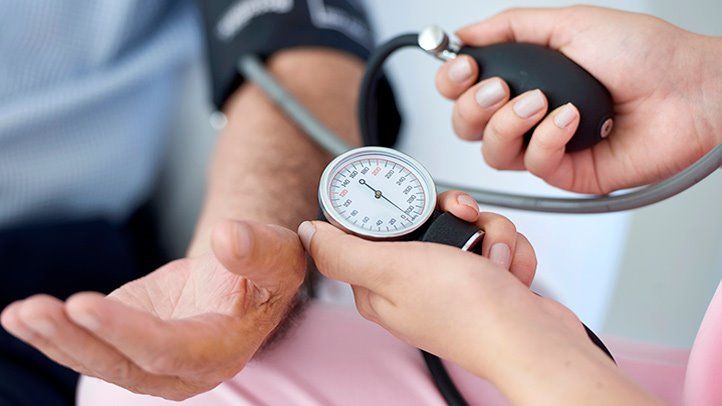

Acupuncture for High Blood Pressure.
High blood pressure (hypertension) and cardiovascular disease has become the most important preventable risk factor for premature deaths worldwide. A normal blood pressure level is around 120/80 mmHg.
Having a high blood pressure increases the risk of heart attacks, stroke, congestive heart failure, kidney failure and erectile dysfunction. More than 90% of high blood pressure cases are categorised as "primary hypertension" which means there is no clear diagnosable cause according to western medicine.
Studies have shown that both acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine may be beneficial as an adjunct therapy for high blood pressure.
What does the research say?
The following insights are obtained from systematic reviews and analysis of clinical trials investigating the efficacy of Chinese medicine and acupuncture for high blood pressure.
2022 Reference Series in Phytochemistry
Coconut water possesses unique compound profiles that imbue it with a broad spectrum of medical properties, incorporating aspects of nutrition, pharmacology, and disease prevention.
The study utilized comprehensive analysis to assess the chemical profile of coconut water, identifying a range of components including phytohormones, enzymes, antioxidant compounds, vitamins, minerals, and phenolic compounds. These components are known to contribute to the water's biological activity and pharmacological effects, thereby enabling a raft of medicinal properties inherent to coconut water. The water was found to feature anti-microbial, anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-hypertensive, rejuvenating, hepatoprotective, hypolipidemic, and diuretic properties.
An examination of the therapeutic effects of coconut water revealed a significant impact on gastric dysfunction, dysentery, and child malnutrition alongside notable capabilities to manage hypertension. The water was found to promote exercise performance, reduce swelling, dissolve kidney stones, improve kidney function, improve digestion, relieve constipation, reduce the risk of heart disease, lower high blood pressure, and improve cholesterol levels. Consumption of tender coconut water was specifically found to reduce the risk of heart disease, help prevent Alzheimer’s disease pathologies and prevent osteoporosis in experimental animals. The unique nutritional profile of coconut water was also found to provide it with the capacity to balance body chemistry and fight cancer.
Health Benefits of Coconut Water Rethinam P, Krishnakumar V
2022 Antioxidants
Pomegranate extract consumption improves antioxidant levels, reduces oxidative stress and cardiovascular risk factors including blood pressure and body fat, and increases lean body mass.
In the study, 24 healthy participants were divided into two groups: one consumed a natural standardized pomegranate extract, while the other, a placebo, in a randomized, single-blind placebo-controlled trial. Evaluations were conducted at baseline and post 14 and 28 days of the experiment, with variables including anthropometric measurements, blood pressure, pulse wave speed, body composition, as well as the levels of salivary and urinary cortisol, cortisone, total phenolics, antioxidant capacity, and lipid peroxidation.
The results indicated significant increases in urinary total phenolics excretion and antioxidant capacity after 14 and 28 days of pomegranate extract intake. By day 28, notable decreases were noted in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, pulse wave velocity, body fat and fat mass, and an increase in lean body mass. In terms of glucocorticoid levels, there was a marked decrease in saliva cortisol at day 28 in the morning for the pomegranate extract group, along with a decrease in the cortisol/cortisone ratio following 28 days of pomegranate extract intake at morning, noon, and evening. Reductions were also seen in urine free cortisol levels by day 14. These observations were unique to the pomegranate extract group, with no significant changes noted in the placebo group.
Antioxidant Properties and Beneficial Cardiovascular Effects of a Natural Extract of Pomegranate in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized Preliminary Single-Blind Controlled Study Al-Dujaili EAS, Casey C, Stockton A
2020 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
This study showed that the intervention time was concentrated at 4–8 weeks, mainly through Chinese herbal medicine for the prevention and treatment of elderly hypertension and the complications.
We systematically retrieved and summarised clinical studies on traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for the prevention and treatment of essential hypertension (EH) using the evidence map. We aimed to explore the evidence distribution, identify gaps in evidence, and inform on future research priorities. Clinical studies, systematic reviews, guidelines, and pathway studies related to TCM for the prevention and treatment of EH, published between January 2000 and December 2019, were included from databases CNKI, WanFang Data, VIP, PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science. The distribution of evidence was analysed using text descriptions, tables, and graphs. A total of 9,403 articles were included, including 5,920 randomised controlled studies (RCTs), 16 guidelines, expert consensus and path studies, and 139 systematic reviews (SRs).
A total of 10 high-quality studies were retrieved, where qigong (20 RCTs), zhengan xifeng decoction (6 RCTs), Liuwei Dihuang pill (6 RCTs), and Chinese herbal medicine (24 RCTs) were considered to have evidence of potential positive effects. Xuefu zhuyu decoction (15 RCTs) was considered a positive effect; i.e., we are confident in estimating the research results.
Traditional Chinese Medicine for Essential Hypertension: A Clinical Evidence Map Zhang Y, Wang B, Ju C, Liu L, Zhu Y, Mei J, Liu Y, Xu F
2020 Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets
Cinnamon supplementation has favorable effects on diastolic blood pressure and long-term effects on systolic blood pressure.
Out of 927 records, 8 trials that enrolled 582 participants were included. The pooled effect size showed that systolic blood pressure did not change following cinnamon supplementation. Also cinnamon supplementation in long-duration (≥ 8weeks) had a significant effect on systolic blood pressure. Pooled analysis showed that cinnamon had a significant effect on diastolic blood pressure. In addition, results from both duration subsets and high dose (>1500 mg/day) of cinnamon supplementation were significant.
What is the Impact of Cinnamon Supplementation on Blood Pressure? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Hadi A, Campbell MS, Hassani B, Pourmasoumi M, Salehi-Sahlabadi A, Hosseini SA.
2019 International Journal of Hypertension
Acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy has antihypertensive effect.
The mechanism of acupuncture for hypertension is related to RAAS, vascular endothelium, oxidative stress, the neuroendocrine system, and other factors; also, there is cross-talk between multiple systems and multiple targets. In addition, the functional images, genes, metabolism, etc. change with antihypertensive effect. Acupuncture can protect target organs in addition to reducing BP. Overall, based on the mechanism research acupuncture may be an effective intervention for management of hypertension.
The Mechanism of Acupuncture in Treating Essential Hypertension: A Narrative Review Juan Li ,1 Mingsheng Sun ,2 Jing Ye,2 Yuxi Li ,2 Rongjiang Jin ,1 Hui Zheng ,2 and Fanrong Liang 2
2019 Journal of Sleep Research
Acupuncture therapy does not impact the severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea, blood pressure, or quality of life in hypertensive patients.
The study examined the effects of acupuncture on blood pressure and Obstructive Sleep Apnea severity in hypertensive patients. These patients, all suffering from mild to moderate Obstructive Sleep Apnea, were randomly divided into two groups, one of which received acupuncture treatment while the other received sham-acupuncture treatment, essentially a placebo. Each patient's condition was assessed before and after ten acupuncture sessions, relying on measures such as polysomnography, around-the-clock blood pressure monitoring, and a life quality survey.
A total of 44 patients completed the study, the group covering both genders, with an average age of 57 years, and a diverse range of body mass indices and apnea-hypopnea indices. It's important to note that there were no distinguishable differences observed in the apnea-hypopnea index, daytime or nighttime blood pressure, or life quality between the group that received genuine acupuncture treatment and the group that received the placebo treatment.
Effects of acupuncture on obstructive sleep apnea severity, blood pressure control and quality of life in patients with hypertension: A randomized controlled trial Silva MVFP, Lustosa TC, Arai VJ, Couto Patriota TLG, Lira MPF, Linsâ€Filho OL, Chalegre ST, B.B.A.S. K, Secundo IV, Pedrosa RP
2017 Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition
Of the 7 clinical trials included, five evaluating individuals with hypertension observed a significant reduction in systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure. The two articles that evaluated individuals with dyslipidemia showed improvement in lipid profile.
The mechanisms of action are still being studied. Regarding the bias risk analysis, clinical trials included showed few descriptions of the methods applied. There are few studies about sesame ingestion, and it was observed high risk for bias in the selected studies. More standardized methods with attention to the design of studies are needed to improve the level of the evidence.
The effect of dietary intake of sesame (Sesamumindicum L.) derivatives related to the lipid profile and blood pressure: A systematic review Carolina Alves Cardoso, Gláucia Maria Moraes de Oliveira, Luciana de Almeida Vittori Gouveia, Annie Seixas Bello Moreira & Glorimar Rosa
2015 PLOS One
There is evidence of efficacy of acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy to western medicine for treating hypertension.
Our review provided evidence of acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy to medication for treating hypertension, while the evidence for acupuncture alone lowing BP is insufficient. The safety of acupuncture is uncertain due to the inadequate reporting of it. However, the current evidence might not be sufficiently robust against methodological flaws and significant heterogeneity of the included RCTs. Larger high-quality trials are required.
Is Acupuncture Effective for Hypertension? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Zhao XF, Hu HT, Li JS, Shang HC, Zheng HZ, Niu JF, et al
2014 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Acupuncture significantly lowers blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications.
Results from this meta-analysis of randomized sham-controlled trials provide evidence that acupuncture helped (lowered) BP in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Our results did not provide support that acupuncture alone significantly lowers BP in patients with hypertension. Larger RCTs with longer follow-up periods would help clarify the potential efficacy and safety of acupuncture for treating hypertension.
Acupuncture for Essential Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Sham-Controlled Clinical Trials Li DZ, Zhou Y, Yang YN, Ma YT, Li XM, Yu J, et al.
2013 Phytotherapy Research
Pomegranate juice intake for two weeks significantly reduces blood pressure and may improve heart health by lowering vascular endothelial adhesion molecule-1 levels.
In the experiment, twenty-one hypertensive participants, aged between 30 to 67 years, were gathered and randomly assigned to consume either 150ml of fresh pomegranate juice per day or an equal quantity of water for a period of two weeks. The pomegranate juice was consumed in a single occasion between lunch and dinner. The blood pressure of these subjects, including systolic and diastolic pressures, were measured before and after the trial period. Additionally, levels of specific elements including lipid profile parameters, apolipoproteins A and B, intracellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular endothelial adhesion molecule 1, E-selectin, and other inflammatory and endothelial function biomarkers such as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, were also measured.
The results showed that the consumption of pomegranate juice was associated with notable reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressures. The intake of pomegranate juice also resulted in a significant decrease in levels of vascular endothelial adhesion molecule 1, even though there was an increase in E-selectin levels. No observable influence appeared on the levels of intracellular adhesion molecule-1, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, lipid profile parameters, apolipoproteins, or interleukin-6 from the juice consumption, indicating that pomegranate juice may specifically target certain elements related to heart health.
Clinical Evaluation of Blood Pressure Lowering, Endothelial Function Improving, Hypolipidemic and Antiâ€Inflammatory Effects of Pomegranate Juice in Hypertensive Subjects Asgary S, Sahebkar A, Afshani MR, Keshvari M, Haghjooyjavanmard S, Rafieianâ€Kopaei M
Consult with our practitioners for personalised care and advice.
Although well-conducted clinical research can help members of the public to make better-informed decisions about their healthcare, we cannot claim that any particular treatment may be effective for any individual person.
When you consult with our Chinese medicine practitioners, you'll receive personalised advice and treatment based on your symptoms and Chinese medicine diagnosis.
Scientific References
Browse our collection of scientific clinical research on acupuncture for high blood pressure.
It includes recent and reputable papers published by peer-reviewed journals within the last 10 years.

2022, Jan
Health Benefits of Coconut Water
Reference Series in Phytochemistry
Coconut water, rich in phytohormones, enzymes, antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and phenolic compounds, exhibits a plethora of medicinal properties, including anti-microbial, anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-hypertensive, rejuvenation, hepatoprotective, hypolipidemic, and diuretic effects. It shows therapeutic potential for gastric dysfunction, dysentery, child malnutrition, and hypertension. Research indicates benefits such as improved exercise performance, reduced swelling, dissolution of kidney stones, enhanced kidney function, improved digestion, relief from constipation, lowered risk of heart disease, reduced high blood pressure, improved cholesterol levels, and prevention of Alzheimer's disease and osteoporosis. Coconut water's unique nutritional profile is suggested to balance body chemistry and potentially contribute to cancer prevention.
Rethinam P, Krishnakumar V Full Article

2022, Oct 28
Antioxidant Properties and Beneficial Cardiovascular Effects of a Natural Extract of Pomegranate in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized Preliminary Single-Blind Controlled Study
Antioxidants
Pomegranate extract intake led to significant increases in urinary total phenolics excretion and antioxidant capacity, along with decreases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, pulse wave velocity, body fat, and fat mass. Additionally, there were improvements in lean body mass and reductions in salivary cortisol levels, suggesting a potential beneficial role in attenuating cardiovascular risk factors.
Al-Dujaili EAS, Casey C, Stockton A Full Article

2020, Dec 19
Traditional Chinese Medicine for Essential Hypertension: A Clinical Evidence Map
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
The conclusion of this systematic review and primary studies highlight TCM's advantages as adjunctive therapy for improving hypertension. Similarly, the development trend of Chinese Medicine and nondrug therapy for the prevention and treatment of hypertension is relatively good, which reflects the diverse TCM prevention and treatment measures for hypertension.
Zhang Y, Wang B, Ju C, Liu L, Zhu Y, Mei J, Liu Y, Xu F Full Article

2020, Jan 20
What is the Impact of Cinnamon Supplementation on Blood Pressure? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets
The present study suggested that cinnamon supplementations improve blood pressure, especially in the long run.
Hadi A, Campbell MS, Hassani B, Pourmasoumi M, Salehi-Sahlabadi A, Hosseini SA. Full Article

2019, Mar 7
The Mechanism of Acupuncture in Treating Essential Hypertension: A Narrative Review
International Journal of Hypertension
Acupuncture can significantly improve cardiac hypertrophy and the thickness of the aortic wall in order to prevent new vascular remodeling .The latest clinical study unveils the cardioprotective effects of acupuncture through improving wave reflection (augmentation index, AIx) and arterial stiffness in hypertensive patient. Therefore, acupuncture is highly essential in treating hypertension
Juan Li ,1 Mingsheng Sun ,2 Jing Ye,2 Yuxi Li ,2 Rongjiang Jin ,1 Hui Zheng ,2 and Fanrong Liang 2 Full Article

2019, Dec 23
Effects of acupuncture on obstructive sleep apnea severity, blood pressure control and quality of life in patients with hypertension: A randomized controlled trial
Journal of Sleep Research
A short course of acupuncture in hypertensive patients under effective antihypertensive treatment with mild to moderate OSA did not reduce OSA severity, or daytime or nocturnal BP, and did not improve quality of life.
Silva MVFP, Lustosa TC, Arai VJ, Couto Patriota TLG, Lira MPF, Linsâ€Filho OL, Chalegre ST, B.B.A.S. K, Secundo IV, Pedrosa RP Full Article

2017, Jun 28
The effect of dietary intake of sesame (Sesamumindicum L.) derivatives related to the lipid profile and blood pressure: A systematic review
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition
Of the 7 clinical trials included, five evaluating individuals with hypertension observed a significant reduction in systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure. The two articles that evaluated individuals with dyslipidemia showed improvement in lipid profile. The mechanisms of action are still being studied. Regarding the bias risk analysis, clinical trials included showed few descriptions of the methods applied. There are few studies about sesame ingestion, and it was observed high risk for bias in the selected studies. More standardized methods with attention to the design of studies are needed to improve the level of the evidence.
Carolina Alves Cardoso, Gláucia Maria Moraes de Oliveira, Luciana de Almeida Vittori Gouveia, Annie Seixas Bello Moreira & Glorimar Rosa Full Article

2015, Jul 24
Is Acupuncture Effective for Hypertension? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
PLOS One Public Library of Science
Our meta-analysis suggested that acupuncture plus western medicine had a more significant effect on both systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure change magnitude than sham acupuncture plus medication, which indicated that acupuncture has an add-on effect for western medicine.
Zhao XF, Hu HT, Li JS, Shang HC, Zheng HZ, Niu JF, et al Full Article

2014, Mar 4
Acupuncture for Essential Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Sham-Controlled Clinical Trials
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
The study is consistent with acupuncture significantly lowers blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Results from this meta-analysis of randomized sham-controlled trials provide evidence that acupuncture helped (lowered) BP in patients taking antihypertensive medications.
Li DZ, Zhou Y, Yang YN, Ma YT, Li XM, Yu J, et al. Full Article

2013, Mar 21
Clinical Evaluation of Blood Pressure Lowering, Endothelial Function Improving, Hypolipidemic and Antiâ€Inflammatory Effects of Pomegranate Juice in Hypertensive Subjects
Phytotherapy Research
Consumption of pomegranate juice for 2 weeks was associated with significant reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, suggesting effective hypotensive effects. Additionally, serum levels of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) were significantly reduced, indicating potential improvement in endothelial function.
Asgary S, Sahebkar A, Afshani MR, Keshvari M, Haghjooyjavanmard S, Rafieianâ€Kopaei M Full Article
“It is by virtue of the twelve channels that human life exists, that disease arises, that human beings can be treated and illness cured. The twelve channels are where beginners start and masters end.” The Classic of Acupuncture
Circa 1st Century BCE








