Acupuncture for Mental Health.
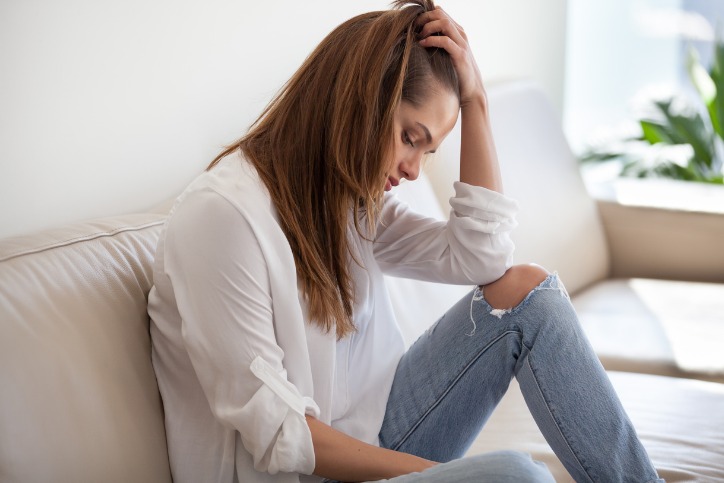
Chronic stress, anxiety and depression are the most common and disabling mental health concerns in modern society. They are often experienced as a complex set of emotional, physical and behavioural symptoms.
People with anxiety disorder frequently experience unpleasant feelings of worry or fear accompanied by physical symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, muscle aches, digestive complaints, trembling, irritability, sweating and hot flashes.
Depression is characterised by low energy, mood and low self-esteem, poor concentration, negative thoughts and emotions, and loss of interest in normally enjoyable activities. Appetite, body weight and sleep are also commonly affected.
What is our clinical experience?
Based on feedback collected from over 2,457 initial appointments for Stress, Anxiety & Depression, 88% of our patients reported improved quality of life after their first 4 appointments. See our detailed benchmarking statistics.
Initial
Consults
2,457
Average
Appointments
4
Improved
Quality of Life
88%
Refer Family &
Friends
91%
What does the research say?
The following insights are obtained from systematic reviews and analysis of clinical trials investigating the efficacy of Chinese medicine and acupuncture for mental health.
2024 The Natural Products Journal
Pumpkin seeds are recognised for their medicinal, nutritional, and cosmetic benefits, including anti-diabetic, heart disease prevention, anti-cancer, and antioxidant qualities.
The review article undertakes a comprehensive exploration of the nutraceutical importance of pumpkin seeds. The methodology includes an examination of the various known substances in the seeds, such as phytoestrogens, unsaturated fatty acids, and vitamin E. The study then delves into the different benefits and therapeutic uses of these components stretching from medicinal to nutritional to cosmetic applications.
The results of this research are diverse and impressive, with implications for several major health sectors. Their potential anti-diabetic and hypoglycemic properties could suggest a significant role in the management and prevention of diabetes. Meanwhile, the seeds' potential in cardiovascular disease prevention could help to address one of the most pressing global health issues. Moreover, potential anti-cancer properties imply that these seeds could even have a part to play in cancer prevention. The review also described potential additional qualities, such as antidepressant, anti-helminthic (parasite-removing), and antioxidant effects.
Pumpkin Seeds (Cucurbita spp.) as a Nutraceutical Used In Various Lifestyle Disorders Wal A, Singh MR, Gupta A, Rathore S, Rout RR, Wal P
2023 Nutrients
Vitamin D deficiency could accelerate depressive symptoms and suicide risks, and vitamin D supplementation may mitigate these effects.
The paper examines the links between vitamin D deficiency, depression, and suicide from various studies. It hypothesizes that vitamin D could enhance serotonin synthesis and modulate proinflammatory cytokines, both factors in depression and suicide. The paper reviews this hypothesis in the context of the broader health issue of suicide, which is among the leading causes of death worldwide.
This paper then discusses the potential benefits of vitamin D supplementation. Drawing upon indirect evidence suggesting that vitamin D deficiencies may be a risk factor for depression—one of the most common factors in suicide attempts—the paper postulates that vitamin D supplementation could play a role in helping to reduce the risk of depression and thus suicide. The beneficial mechanisms of vitamin D, such as enhancing serotonin synthesis and modulating proinflammatory cytokines, which are associated with depression and suicide, stand as the central contributing factors in this hypothesis.
Vitamin D in Depression: A Potential Bioactive Agent to Reduce Suicide and Suicide Attempt Risk Somoza-Moncada MM, Turrubiates-Hernández FJ, Muñoz-Valle JF, Gutiérrez-Brito JA, DÃaz-Pérez SA, Aguayo-Arelis A, Hernández-Bello J
2023 Sleep Medicine Clinics
Acupuncture may enhance the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy for people suffering from insomnia and related conditions.
The research methodology used in this paper is mainly a theoretical analysis and discussion of the potential synergistic effects of combining cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) and acupuncture. This involves analysis of the current evidence base for the efficacy of acupuncture in treating insomnia and related conditions, along with examination of the practical, logistical, and regulatory aspects of combining these two treatments.
In the discussion of their results, the researchers found that there is a growing body of evidence that supports the potential benefit of acupuncture in treating insomnia and its comorbidities, enhancing the current standard treatment approach of CBT-I. This appears to be an innovative approach that could potentially enhance the treatment effectiveness and outcomes for those struggling with insomnia, though it concurrently raises complex issues in terms of its practical and regulatory implementation.
Acupuncture as an Adjunct Treatment to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia Kutana S, Mao JJ, Garland SN
2023 Journal of Functional Foods
Fermented Pueraria lobata root extract and Glycine max extract showed estrogen-like activities, reducing depressive symptoms in menopausal mice but not increasing female cancer risks.
The researchers focused on Pueraria lobata roots and Glycine max (also known as soybeans) extracts, which are rich in isoflavones but often limited in practical use due to their high molecular weight and low bioavailability. The researchers chose to ferment these extracts with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains which are known to convert glycosides to aglycones, potentially enhancing the beneficial effects of the isoflavones. Specifically, the study was conducted using ovariectomized mice.
The research found that both fermented Pueraria lobata root extract and Glycine max extract exhibited estrogen-like activities. More intriguingly, the fermentation process increased the expression of estrogen receptor beta, suggesting that these extracts may not increase the risk of various female cancers—a common side effect of hormone replacement therapy—as was previously believed. Also, the ingestion of these extracts not only increased the estrogen receptor beta in the mice but also upregulated the expression of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampal region of the brain, thus improving depressive symptoms. The highest expression was observed in the group given a mixture of both extracts.
Effects of Pueraria lobata root and Glycine max (L.) Merrill extracts fermented with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the depressive-like behavior in ovariectomized mice via upregulation of hippocampal BDNF Ha J, Jang HM, Choi I
2022 Research in Nursing & Health
Acupuncture, either in isolation or as an adjunct to pharmacological treatment, has clinical benefits and can be considered a safe option for managing depression.
A review of 22 trials involving 2,391 participants found that acupuncture can reduce depression severity. Combining acupuncture with antidepressants was more effective than using antidepressants alone or waitlist. However, acupuncture alone or with antidepressants didn't show significant benefits compared to sham acupuncture. Sham acupuncture might have stronger effects than other placebos. Differences in treatment sessions and cultural backgrounds between China and Western countries affect outcomes. Lack of standardization in acupuncture regimens hinders research. Mild adverse events were reported but need better documentation.
Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for depression: A systematic review and metaâ€analysis Chen B, Wang CC, Lee KH, Xia JC, Luo Z
2022 Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies
Acupuncture shows promise in improving psychiatric symptoms, physical symptoms, and quality of life in patients with treatment-resistant mood disorders, highlighting its potential as a complementary therapy for these conditions.
This prospective study explored the effects of acupuncture on physical symptoms and quality of life (QoL) in patients with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD) and bipolar disorder (BD). After 12 weeks of acupuncture treatment, significant improvements were observed in psychiatric symptoms, physical symptoms, and various aspects of QoL. These findings suggest that acupuncture may be beneficial for both the physical and mental well-being of patients with treatment-resistant mood disorders, although further research is needed to validate these preliminary results.
Effect of Acupuncture on Physical Symptoms and Quality of Life in Treatment-Resistant Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder: a Single-Arm Longitudinal Study Matsuura Y, Hongo S, Taniguchi H, Yasuno F, Sakai T
2022 Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies
Acupuncture shows promise in improving psychiatric symptoms, physical symptoms, and quality of life in patients with treatment-resistant mood disorders, highlighting its potential as a complementary therapy for these conditions.
This prospective study explored the effects of acupuncture on physical symptoms and quality of life (QoL) in patients with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD) and bipolar disorder (BD). After 12 weeks of acupuncture treatment, significant improvements were observed in psychiatric symptoms, physical symptoms, and various aspects of QoL. These findings suggest that acupuncture may be beneficial for both the physical and mental well-being of patients with treatment-resistant mood disorders, although further research is needed to validate these preliminary results.
Effect of Acupuncture on Physical Symptoms and Quality of Life in Treatment-Resistant Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder: a Single-Arm Longitudinal Study Matsuura Y, Hongo S, Taniguchi H, Yasuno F, Sakai T
2022 Frontiers in Pharmacology
Xiao Yao San has potential as an effective and safe alternative treatment for depression, offering multiple mechanisms of action for its antidepressant effects.
The article discusses the use of Xiaoyaosan, a traditional Chinese medicine formulation, in the treatment of depression. It reviews recent evidence from animal and clinical studies, highlighting the pharmacological mechanisms and effective components involved in the antidepressant effects of Xiaoyaosan. The review explores various factors such as neurotransmitters, neuroplasticity, inflammatory response, gut-brain axis, oxidative stress, and autophagy that contribute to its therapeutic effects. The article emphasizes the potential of Xiaoyaosan as an alternative therapy for depression and provides an overview of its mechanisms of action.
Research progress on classical traditional chinese medicine formula xiaoyaosan in the treatment of depression Chen J, Lei C, Li X, Wu Q, Liu C, Ma Q, Chen J.
2022 Medicine
High prevalence of insomnia, anxiety, and depression among perimenopausal women, emphasizing the importance of exploring acupuncture as a potential green therapy for effectively addressing these interconnected issues.
This passage discusses the prevalence of insomnia among perimenopausal women, its association with anxiety and depression, and the potential of acupuncture as a green therapy for treating these issues. The passage outlines the objectives and methods of a systematic review aiming to evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture in improving sleep quality and alleviating anxiety and depression in perimenopausal women, highlighting the need for safer alternatives to conventional medications and the significance of such a study.
Can acupuncture improve sleep quality and anxiety among women during perimenopause? Ping Y, Liang C, Fan X, Zhang L, Ying D, Wang Z
2022 Medicine
High prevalence of insomnia, anxiety, and depression among perimenopausal women, emphasizing the importance of exploring acupuncture as a potential green therapy for effectively addressing these interconnected issues.
This passage discusses the prevalence of insomnia among perimenopausal women, its association with anxiety and depression, and the potential of acupuncture as a green therapy for treating these issues. The passage outlines the objectives and methods of a systematic review aiming to evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture in improving sleep quality and alleviating anxiety and depression in perimenopausal women, highlighting the need for safer alternatives to conventional medications and the significance of such a study.
Can acupuncture improve sleep quality and anxiety among women during perimenopause? Ping Y, Liang C, Fan X, Zhang L, Ying D, Wang Z
2022 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Xiao Yao San, alone or combined with anxiolytics, assists in better improvement and safety in treating anxiety disorders compared to anxiolytics alone.
The methodology involved a systematic search on PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, Web of Science, and several Chinese databases for all randomized control trials (RCTs) that have evaluated the use of XYS for treating anxiety disorders until November 2021. The studies were independently screened, and data were extracted by two investigators who also assessed the risk of bias in the selected trials using RevMan5.3 software.
The meta-analysis result shows that the use of XYS, either on its own or together with anxiolytics, showed better improvements in anxiety-related symptoms and fewer adverse drug reactions compared to treatment with anxiolytics only. This suggests that XYS, whether used alone or in conjunction with anxiolytic agents, appears to offer a more effective and safer treatment option for anxiety disorders.
Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of Xiao Yao San as a Treatment for Anxiety: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Lin J, Ji Y, Si J, Wang G, Li X, Shen L
2022 Annals of Medicine
The Gui Zhi-Shao Yao herb pair in traditional Chinese medicine potentially treats chronic pain, anxiety, and depression through interactions with nine key targets.
The methodology in this research utilised network pharmacology to explore the active components of the "Gui Zhi-Shao Yao" herb pair and their possible targets. Initially, 15 active compounds were identified through a series of analysis which revealed about 130 potential targets. By considering the intersections between the targets of the "Gui Zhi-Shao Yao" herb pair and chronic pain, anxiety disorder, and mental depression, nine vital targets were identified and listed in order of importance.
The results discussion revealed that the "Gui Zhi-Shao Yao" herb pairing acted on the nine identified key targets to alleviate chronic pain, anxiety, and depression. Gene ontology and pathway analysis demonstrated that there were 11 primary pathways, including AGE-RAGE signalling pathway, IL-17 signalling pathway, and TNF signalling pathway. These pathways appear to be actively involved in the pathological processes, providing a holistic understanding of how the "Gui Zhi-Shao Yao" herb pair functions therapeutically.
A network pharmacology approach to predict potential targets and mechanisms of “Ramulus Cinnamomi (cassiae) – Paeonia lactiflora†herb pair in the treatment of chronic pain with comorbid anxiety and depression Pan HT, Xi ZQ, Wei XQ, Wang K
2022 Annals of Medicine
The Gui Zhi-Shao Yao herb pair in traditional Chinese medicine potentially treats chronic pain, anxiety, and depression through interactions with nine key targets.
The methodology in this research utilised network pharmacology to explore the active components of the "Gui Zhi-Shao Yao" herb pair and their possible targets. Initially, 15 active compounds were identified through a series of analysis which revealed about 130 potential targets. By considering the intersections between the targets of the "Gui Zhi-Shao Yao" herb pair and chronic pain, anxiety disorder, and mental depression, nine vital targets were identified and listed in order of importance.
The results discussion revealed that the "Gui Zhi-Shao Yao" herb pairing acted on the nine identified key targets to alleviate chronic pain, anxiety, and depression. Gene ontology and pathway analysis demonstrated that there were 11 primary pathways, including AGE-RAGE signalling pathway, IL-17 signalling pathway, and TNF signalling pathway. These pathways appear to be actively involved in the pathological processes, providing a holistic understanding of how the "Gui Zhi-Shao Yao" herb pair functions therapeutically.
A network pharmacology approach to predict potential targets and mechanisms of “Ramulus Cinnamomi (cassiae) – Paeonia lactiflora†herb pair in the treatment of chronic pain with comorbid anxiety and depression Pan HT, Xi ZQ, Wei XQ, Wang K
2022 Natural Product Communications
Combining traditional Chinese medicine may offer potential therapeutic value in treating both Alzheimer's disease and major depressive disorder simultaneously.
Researchers leveraged network pharmacology and molecular docking technology to identify the effect of traditional Chinese medicine and its multitarget components for treating Alzheimer's disease and major depressive disorder. They analyzed 234 TCM prescriptions for major depressive disorder, identifying the top 10 most commonly used herbs, reflecting 198 active ingredients. They then did comparative analysis for prospective ingredient targets related to both disorders. The analysis included exploring common and key targets and representative compounds for effective treatment. The combination of Xiangfu (Cyperi Rhizoma), Gancao (Licorice) and Chaihu (Radix Bupleuri) constituted the major component of representative ingredients that were analyzed.
The results yielded the identification of 30 common targets, 9 key targets, and 7 representative compounds relevant to both disorders. Their findings revealed these common targets were essential to regulate multiple pathways linked to both disorders, emphasizing the potential for a cohesive treatment approach. Furthermore, molecular docking studies unveiled the binding affinity of several natural chemicals, including quercetin, kaempferol, β-sitosterol, stigmasterol, isorhamnetin, naringenin, and 8-isopentenyl-kaempferol, with key prospective targets. This suggests that a TCM combination could provide therapeutic advantages in treating both Alzheimer's disease and major depressive disorder.
Screening Traditional Chinese Medicine Combination for Co-Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease and Major Depressive Disorder by Network Pharmacology Huang Z, Fang Y, Wang X, Wang Q, Wang T
2022 Frontiers in Psychiatry
Acupuncture can be a safe and effective alternative therapy to conventional drugs for improving sleep quality and relieving symptoms in patients with active depression.
The research methodology involved a systematic review of randomized controlled trials focusing on the effect of acupuncture on depression-related insomnia. These studies were identified from seven different databases, dating up until December 2021. The papers included compared acupuncture to controls (waiting list or placebo/sham acupuncture) and conventional treatments (Western pharmacotherapy and/or cognitive-behavioral therapy) either alone or in combination with acupuncture. The analysis followed Cochrane criteria and encompassed a total of 21 trials, including 1,571 participants.
Regarding results, it was found that acupuncture significantly reduced severity metrics of sleep quality and depression for patients who have active depression, compared with placebo-acupuncture. When contrasted with standard care (antidepressants and/or sleeping aids), acupuncture led to improvements in sleep quality and depressive symptom scores. However, for those suffering from the lingering symptoms of past or partially treated depression, the therapeutic benefits of acupuncture were minor and not statistically noteworthy. Unfortunately, no studies were found to review acupuncture's efficacy compared to cognitive-behavioral therapy or its potential synergistic effect when used concurrently.
The Role of Acupuncture in the Management of Insomnia as a Major or Residual Symptom Among Patients With Active or Previous Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Zhao FY, Kennedy GA, Spencer SJ, Conduit R, Zhang WJ, Fu QQ, Zheng Z
2022 Plants
The traditional Chinese medicine Gan Mai Da Zao Tang may lessen depressive behaviors in rats, likely through licorice increasing serotonin transporter and brain-derived neurotrophic factor signals in the hippocampus.
This study experimentally examined the antidepressant impacts of Gan-Mai-Da-Zao (GMDZ), a Chinese traditional medicine that contains blighted wheat, licorice, and jujube. The researchers used an unpredictable chronic mild stress model in rats, some of whom received an injection with p-chlorophenylalanine to generate a chemical model for depression. The investigators employed behavioral tests, including forced swim tests, open field tests, and sucrose preference tests, to evaluate the chronic influence of GMDZ.
The oral application of GMDZ over 21 days considerably eased depressive behaviors in rats induced by either the unpredictable chronic mild stress or p-chlorophenylalanine. The treatment increased the expression of the serotonin transporter and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus in the rats with depression. However, rats provided with a similar herbal mixture that did not include licorice showed a significantly worse response, suggesting that licorice may play an essential role in the efficacy of GMDZ in combatting depression-like behaviors.
Major Plant in Herbal Mixture Gan-Mai-Da-Zao for the Alleviation of Depression in Rat Models Li YX, Cheng KC, Hsu CT, Cheng JT, Yang TT
2022 Frontiers in Neuroscience
Chinese herbal medicine shows promising and safe outcomes in relieving functional dyspepsia symptoms and associated psychological disorders.
The methodology for this research involved a comprehensive search across various libraries and databases, such as PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and various Chinese data sources, seeking randomized controlled trials where functional dyspepsia was treated with Chinese herbal medicine. The aim was to assess the efficacy and safety of this type of treatment for functional dyspepsia. Two researchers independently conducted each stage of the process, from searching the sources, screening the documents, extracting data, and assessing risk biases within the included studies. They used RevMan 5.4 software to do a meta-analysis of the selected research materials.
The discussion of their findings showed that treatment with Chinese herbal medicine significantly alleviated the symptoms of functional dyspepsia, compared to both a placebo group and a group treated with traditional prokinetic agents and flupentixol melitracen. Patients treated with Chinese herbal medicine reported higher total effective rates and lower total symptom scores, along with smaller depression and anxiety scores. The symptoms of functional dyspepsia, in this case, were improved more successfully with Chinese herbal medicine than with other treatment types, without any significant adverse reactions.
Chinese Herbal Medicine for Functional Dyspepsia With Psychological Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Luo X, Wang L, Fang S, Qing X, Jiang T, Yang Y, Su X, Wei W
2022 Frontiers in Neuroscience
Chinese herbal medicine shows promising and safe outcomes in relieving functional dyspepsia symptoms and associated psychological disorders.
The methodology for this research involved a comprehensive search across various libraries and databases, such as PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and various Chinese data sources, seeking randomized controlled trials where functional dyspepsia was treated with Chinese herbal medicine. The aim was to assess the efficacy and safety of this type of treatment for functional dyspepsia. Two researchers independently conducted each stage of the process, from searching the sources, screening the documents, extracting data, and assessing risk biases within the included studies. They used RevMan 5.4 software to do a meta-analysis of the selected research materials.
The discussion of their findings showed that treatment with Chinese herbal medicine significantly alleviated the symptoms of functional dyspepsia, compared to both a placebo group and a group treated with traditional prokinetic agents and flupentixol melitracen. Patients treated with Chinese herbal medicine reported higher total effective rates and lower total symptom scores, along with smaller depression and anxiety scores. The symptoms of functional dyspepsia, in this case, were improved more successfully with Chinese herbal medicine than with other treatment types, without any significant adverse reactions.
Chinese Herbal Medicine for Functional Dyspepsia With Psychological Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Luo X, Wang L, Fang S, Qing X, Jiang T, Yang Y, Su X, Wei W
2022 Frontiers in Pharmacology
Modified Xiao Chai Hu Decoction combined with mirtazapine shows superior effectiveness in treating persistent depressive disorder compared to traditional Chinese medicine alone.
For the study, patients from the Naval General Hospital diagnosed with persistent depressive disorder were selected and divided into two groups. One group received modified Xiaochaihu Decoction only, while the other group was treated with a combination of modified Xiaochaihu Decoction and mirtazapine. To track progress, measurements were taken using the self-rating depression scale and the traditional Chinese medicine scale at the beginning of treatment, and again after a period of 12 weeks. Moreover, an account of any adverse reactions was also kept.
The study results indicate the total effective rate was significantly higher in the combined group compared to the control group. It was also found that while post-treatment scores of the depression scales were lower in both groups, the difference between the groups was not statistically significant. However, the combined group reported higher improvement rates for symptoms like insomnia, bitter taste, languid, and belching/anorexia. An increased frequency of adverse events was also noted in the combined group.
Modified Xiaochaihu Decoction Combined with Mirtazapine in the Treatment of Persistent Depression: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial Xin Li, Xiuyu Li, Man Gong, Chaoqun Li, Jing Li, Chao Zhou, Tingting He
2022 Journal of Ethnopharmacology
Xiang Fu, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine, shows significant antidepressant effects.
The study reviewed the major antidepressant mechanisms and clinical applications of Cyperi Rhizoma, known as CR. It aimed to evaluate the pharmacological effects and the chemical compositions associated with these effects. The authors underwent an extensive literature search using "Cyperus rotundus L." as the search term across multiple electronic databases including Web of Science, ScienceDirect, and PubMed.
In discussing the results, the researchers found that CR has broad application in alleviating symptoms related to stagnation of Qi, such as issues with the liver, stomach, and bowels, common in different countries. They identified the effective constituents of CR, including Aqueous extract, EtOH extract, essential oil, total oligomeric flavonoids, and five other extracts. These exhibited various pharmacological activities, such as antibacterial, antioxidant, neuroprotective, antihemolytic, and anti-inflammatory effects. Notably, specific components like α-cyperone and nootkatone showed antidepressant effects. Through synthesizing this scientific information, they concluded that CR holds potential as a herbal medicine to develop antidepressant drugs with fewer side effects.
The association study of chemical compositions and their pharmacological effects of Cyperi Rhizoma (Xiangfu), a potential traditional Chinese medicine for treating depression Lu J, Li W, Gao T, Wang S, Fu C, Wang S
2022 Nutrients
Eating two gold kiwifruit daily can lead to significant improvements in mood and energy, thereby boosting psychological well-being in adults.
The study conducted a literature review through databases like CINAHL, Embase, and PubMed, searching for English language articles published from 2005 to July 2022. These articles had to be randomized trials involving kiwifruit interventions targeting adults and assessing psychological well-being. The researchers used the Joanna Briggs Institute's critical appraisal tool to evaluate potential bias in these trials. After the search, they selected two suitable trials involving 202 participants.
In discussing the results, the evidence found shows that regularly consuming two gold kiwifruits daily was linked with a significant decrease in mood disturbance and fatigue, and a significant increase in vigor and overall well-being. These effects were more pronounced in participants who had more significant initial mood disturbances. The study concluded by underlining the potential utility of consuming gold kiwifruit daily to promote improved psychological health.
The Role of Kiwifruit in Supporting Psychological Well-Being: A Rapid Review of the Literature Billows M, Kakoschke N, Zajac IT
2022 Explore: The Journal of Science & Healing
Inhalation aromatherapy using lavender and chamomile essential oils effectively reduces depression, anxiety, and stress levels in community-dwelling older adults.
From a methodological perspective, the researchers adopted a three-armed, parallel, randomized, and controlled trial design. A total of 183 participants were enrolled in the study and were randomly divided into three groups: lavender, chamomile, and control group with equal numbers in each. The individuals in the experimental groups were given three drops of 1.5% lavender and chamomile essential oils to inhale for 30 consecutive nights, while the control group inhaled distilled water in the same manner. The Depression, Anxiety, and Stress-Scale (DASS) was utilized to collect data both prior to the intervention, directly following the intervention, and a month after the treatment.
In terms of the results gathered, there was significant improvement in the depression, anxiety, and stress levels of individuals in the lavender and chamomile groups both immediately and one month after the treatment compared to the control group. This indicates that inhalation aromatherapy utilizing lavender and chamomile essential oils can be efficacious in reducing mental health issues among older adults residing in the community.
The effects of Lavender and Chamomile essential oil inhalation aromatherapy on depression, anxiety and stress in older community-dwelling people: A randomized controlled trial Ebrahimi H, Mardani A, Basirinezhad MH, Hamidzadeh A, Eskandari F
2022 Medicina
Chaihu Shugan powder, a traditional Chinese medicine, presents potential advantages in treating post-stroke depression, showing potential as an alternative to conventional antidepressants.
The research approach merges both clinical and experimental studies in exploring the effectiveness of Chaihu Shugan powder, a classic traditional Chinese medicine formula, in treating post-stroke depression. Starting from current clinical cases, the study thoroughly investigates the mechanisms of action and drug and chemical effects of this treatment. The attention is given to the performance of Chaihu Shuan powder in counteracting post-stroke depression, focusing on patients who have not shown an adequate response or experienced adverse reactions to commonly used antidepressants like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors.
The results indicate outstanding benefits of the Chinese herbal treatment for post-stroke depression. It shows that Chaihu Shugan powder could potentially offer a significant contribution to incapacity and recovery of cognitive dysfunction and motor function after a stroke. It also helps to prominently lessen the probability of neurovascular events coming back. This highlights the values of Chaihu Shugan powder that serves as an effective and promising alternative to the standard drug treatments for post-stroke depression.
A Chinese Classical Prescription Chaihu Shugan Powder in Treatment of Post-Stroke Depression: An Overview Gao Z, Wang Y, Yu H
2022 Frontiers in Pharmacology
Chinese herbal medicine shows evident efficacy in treating coronary heart disease patients with anxiety or depression, notably improving symptoms of angina pectoris.
Method: The study was conducted through a systematic approach, wherein literature search was performed based on certain screening studies. Information was extracted by two researchers who independently assessed the quality of the articles. These articles covered numerous studies concerning the active ingredients of Chinese herbal medicine utilized for treating coronary heart disease accompanied by anxiety or depression. The analysis of this data was performed through network pharmacology.
Results: According to 32 chosen studies, Chinese herbal medicine was found to be markedly beneficial in treating anxiety or depression in patients who also had coronary heart disease. This was true in comparison to blank control groups, and the efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine appeared not to be inferior to that of Western medicine. Chinese herbal medicine also significantly enhanced angina stability. Observations after usage of Chinese herbal medicine demonstrated similar trends in terms of angina frequency and electrocardiogram analysis. From the network pharmacology viewpoint, a set of certain compounds were found to possess the greatest correlation to the pathological targets of coronary heart disease, anxiety, and depression. Anti-damage or apoptosis, anti-inflammation, oxidative stress reduction, and maintaining neurotransmitter homeostasis were believed to be the principal functional mechanisms.
Evidence and Characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Coronary Heart Disease Patients With Anxiety or Depression: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review Wang B, Teng Y, Li Y, Lai S, Wu Y, Chen S, Li T, Han X, Zhou H, Wang Y, Lu Z, Li H, Ding Y, Ma L, Zhao M, Wang X
2021 Annals of General Psychiatry
Acupuncture therapy aimed at reducing anxiety in patients with generalised anxiety disorder has certain beneficial effects compared to controls.
Twenty RCTs were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis. All included studies were designed for patients with generalised anxiety disorder (GAD), and 18 studies were published in Chinese. Egger’s test showed that the asymmetry of the funnel plot in all studies was not significant. The meta-analysis of anxiety symptoms showed that acupuncture was more effective than the control condition, with a standard mean effect size of − 0.41, and that acupuncture intervention showed good tolerance and safety in the treatment of anxiety disorder.
Effectiveness of acupuncture on anxiety disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials Yang, Xy., Yang, Nb., Huang, Ff. et al.
2021 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
The comprehensive evaluation results show that scalp acupuncture is effective in treating insomnia.
A total of 21 studies were included in this study, and a total of 1606 cases were included. The comprehensive evaluation results show that scalp acupuncture is effective in treating insomnia. Compared with the control group, scalp acupuncture can significantly improve the effective rate of treating insomnia. The PSQI score subgroup analysis showed that the PSQI score of the head was significantly better than that of the drug and blank group, but there was no significant difference from other acupuncture methods. Sensitivity analysis showed that scalp acupuncture ameliorates the PSQI score better, but excluding any item had high heterogeneity. Meta regression analysis of PSQI score according to different intervention measures in the control group showed that the difference of intervention measures in the control group was the source of heterogeneity. In terms of adverse events, the scalp acupuncture group had no adverse events, which was significantly better than the control group. Based on this study, we found that scalp acupuncture is effective and safe in the treatment of insomnia.
Efficacy and Safety of Scalp Acupuncture for Insomnia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Fu-gui Liu, Ai-hua Tan, Chao-qun Peng, Yun-xia Tan, Ming-chao Yao
2021 Physiology & Behavior
Combining resistance training with saffron supplementation enhances happiness levels and increases dopamine and serotonin concentrations more than resistance training alone.
In this research, untrained young males were divided into two groups, one receiving resistance training coupled with saffron supplementation (150 mg pill of pure saffron post-workout and at a similar time on rest days), while the other received resistance training with a placebo (dextrose pill). For a period of six weeks, whole-body supervised resistance training was performed four times per week with three sets using 60-70% of their single repetition maximum. Various markers implicated in depression and happiness levels were assessed before and after this period.
In terms of results, substantial increases in various markers including Anandamide, Arachidonoylglycerol, dopamine, and beta-endorphin were noticed within the group combining resistance training with saffron supplementation, yet no such changes were evident within the group who took the placebo. Compared to the placebo, the saffron group also experienced more significant improvements in happiness levels. Moreover, serotonin levels increased in both groups but were greater in the saffron-supplemented group, while tryptophan concentrations remained unchanged. Notably, both groups noted significant boosts in muscular endurance; these changes were greater with saffron supplementation.
Impact of saffron (Crocus Sativus Linn) supplementation and resistance training on markers implicated in depression and happiness levels in untrained young males Moghadam BH, Bagheri R, Roozbeh B, Ashtary-Larky D, Gaeini AA, Dutheil F, Wong A
2021 Trends in Food Science & Technology
Coconut oil has potential therapeutic value in treating Alzheimer's disease by suppressing neuro-inflammation, reversing neurodegeneration, and inhibiting secretion of harmful peptides.
The methodology of this study hinges on investigating the impact of coconut oil-derived medium chain fatty acids (MCFAs) on brain glucose metabolism, which is linked to Alzheimer's Disease (AD). These MCFAs rapidly metabolize into ketone bodies, possibly providing alternative energy for cerebral tissue. This research evaluates the recent findings on the role of coconut oil in mitigating AD symptoms, including its dietary effects on reducing neuro-inflammation, reversing neurodegenerative processes, and inhibiting the secretion of amyloid β peptides, which contribute to AD.
The results of the investigation reveal a promising correlation between coconut oil and the amelioration of AD symptoms. The effectiveness of coconut oil is believed to be due to its ability in enhancing cell survival pathways, suppressing neuro-inflammation, and reversing neurodegeneration. Coconut oil also proves useful in preventing the secretion of harmful amyloid β peptides, as seen in animal models and human clinical trials. These multi-pronged biochemical effects underline the immense therapeutic potential of coconut oil in treating AD.
Dietary prospects of coconut oil for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD): A review of recent evidences Ramesh SV, Krishnan V, Praveen S, Hebbar KB
2021 Journal of Trauma Nursing
Auricular acupressure may be a safe and effective technique for reducing burnout and secondary traumatic stress in healthcare workers.
In this prospective randomized trial with an open, parallel-group design, participants were randomized to receive one of three interventions: auricular acupuncture, auricular seed acupressure, or auricular massage. Interventions took place over a period of 3 weeks at a 334-bed Level II pediatric trauma center. Using a pre-/posttest design, the researchers analyzed self-reported scores from the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory, the Professional Quality of Life scale, and the Caring Ability Inventory.
The study found that auricular seed acupressure was associated with a reduction in burnout and secondary traumatic stress. Importantly, this effect remained even after adjusting for individual pretest scores. Attempts at achieving significant effects on anxiety levels, professional quality of life, and caring ability, however, did not yield any significant improvement. Overall, the data suggest that auricular acupressure is a very effective strategy for reducing work-related stress among health care staff.
Effects of Acupuncture and Acupressure on Burnout in Health Care Workers: A Randomized Trial Afrasiabi J, McCarty R, Hayakawa J, Barrows J, Lee K, Plouffe N, Schomberg J
2020 Annals of Palliative Medicine
Acupuncture treatment of insomnia is efficacious, not because of its placebo effect.
Acupuncture is a common alternative therapy for clinical treatment of insomnia. As the underlying mechanism is yet unclear, its efficacy is often considered as placebo effect. To clarify whether acupuncture treatment of insomnia is only due to its placebo effect, a systematic review and a meta-analysis were designed based on the comparison between acupuncture and sham acupuncture.
Compared to the sham groups, acupuncture significantly decreased the PSQI score (P<0.0001). A subgroup analysis showed that the selection of sham acupuncture methods did not affect the results of PSQI. A subgroup of two trials with a total of 141 participants with major depressive disorder did not show any significant reductions in total PSQI scores (P=0.11). In addition, a significant difference was detected in the change of Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) scores (362 adult patients, 4 trials) between acupuncture and sham acupuncture (P<0.0001). The PSG and actigraphy data from acupuncture and the sham did not reveal any significant differences in the sleep structure changes.
For the selection of sham acupuncture, both methods performed similarly in a clinical setting. Moreover, insomnia patients with major depression disorder were not recommended to use only acupuncture treatment.
Placebo effect of acupuncture on insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis Liu C, Xi H, Wu W, Wang X, Qin S, Zhao Y, Zheng S, Wan Q, Xu L.
2020 Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment
Acupuncture is associated with a reduction in the risk of depression during long-term follow-up in patients with trigeminal neuralgia.
In total, 776 patients with newly diagnosed trigeminal neuralgia in each cohort with similar baseline characteristics were enrolled in the study. The acupuncture cohort had a reduced risk of depression compared to the non-acupuncture cohort. Kaplan–Meier analysis also revealed that the cumulative incidence of depression was significantly lower in the acupuncture cohort during the 13-year follow-up period. In particular, the beneficial effect of acupuncture was a decrease in the risk of depression among TN patients aged 50– 69 years who had also used carbamazepine.
Long-Term Beneficial Effects of Acupuncture with Reduced Risk of Depression Development Following Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study Liao CC, Lin CL, Liao KR, Li JM
2020 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
In the treatment of chronic pain with depression, acupuncture could not only achieve better clinical efficacy, but also have higher safety compared with conventional mediation therapy.
Acupuncture has a promising application prospect due to its unique advantages for the treatment of chronic pain with depression comorbidity, which can be used in patients suffering from some certain chronic pain with depression comorbidity with poorer response to the conventional medication or suffering from serious side effects.
Effect of Acupuncture on Chronic Pain with Depression: A Systematic Review Yan B, Zhu S, Wang Y, Da G, Tian G
2020 Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience
Acupuncture appears to be a promising complementary treatment for Alzheimer's disease, according to findings from systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
The study analysed the role of acupuncture as a complementary treatment for Alzheimer's disease by perusing systematic reviews and meta-analyses using data from eight electronic databases. The researchers employed a variety of tools such as the Assessing the Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews 2, Risk of Bias in Systematic Reviews tool, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses, and the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation to determine the quality of methodology, risk of potential bias, and quality of the evidence.
A total of eleven systematic reviews and meta-analyses met the necessary criteria for inclusion in this study. The results, despite indicating that acupuncture may show promise as a complementary treatment for Alzheimer's disease, all rated critically low in quality when assessed with the tools employed. Some methodological weaknesses remained, particularly pertaining to the protocol and registration, search strategy, risk of bias, additional analyses, and funding. Only a small portion of the reviews exhibited a low risk of bias. There was no high-quality evidence found, but moderate-quality evidence was provided for seven outcomes. The risk of bias in the original trials seemed more prevalent than inconsistency, imprecision, and publication bias.
Acupuncture for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: An Overview of Systematic Reviews Huang J, Shen M, Qin X, Wu M, Liang S, Huang Y
2020 Nutrients
Daily supplementation of Matcha Green Tea Powder is found to enhance cognitive functions in elderly women.
The research performed a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial over a period of 12 weeks. The involvement of 61 participants who were community-dwelling elderly people was arranged, and these participants were randomly assigned to either a test group receiving a daily drink containing 3 grams of Matcha Green Tea Powder or a placebo group. Assessments of their cognitive function changes were made using a psychometric test battery. Also, the participants' daily food intake was monitored and recorded using a Brief-type Self-administered Diet History Questionnaire.
The results clearly indicated substantial enhancement in cognitive functions in women who were part of the active test group. It was observed in the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scoring scheme. An interesting pattern that came up in the dietary analysis was the significant inverse correlation between consumption of vitamin K in everyday food apart from test drinks and a change in MoCA. Overall, the study indicates that regular intake of Matcha Green Tea Powder can have protective effects against cognition decline, particularly in elderly women residing in the community.
Effects of Matcha Green Tea Powder on Cognitive Functions of Community-Dwelling Elderly Individuals Sakurai K, Shen C, Ezaki Y, Inamura N, Fukushima Y, Masuoka N, Hisatsune T
2020 Integrative Cancer Therapies
Tian Wang Bu Xin Dan can potentially alleviate symptoms of cancer-related insomnia similarly to cognitive-behavioral therapy.
In this study, 22 participants were divided equally between a group given Cheonwangbosimdan and a control group who received cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia. Participants in the Cheonwangbosimdan group were required to consume the herbal liquid daily and participate in weekly visits for a period of four weeks. Conversely, the control group underwent behavioral therapy sessions 4 times over the same four-week period.
The outcomes from these interventions were evaluated using key indices that measured participants' insomnia severity, sleep quality, fatigue, anxiety, and overall performance status. With the focus being on changes observed from the inception of the trial to the end, these measurements were taken at the conclusion of the fifth week. While no significant difference was found between the two study groups, both displayed a positive trend towards alleviating the symptoms of cancer-related insomnia, with anxiety levels markedly lower in the treatment group.
Comparative Effectiveness of Cheonwangbosimdan (Tian Wang Bu Xin Dan) Versus Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia in Cancer Patients: A Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Parallel-Group, Pilot Trial Moon SY, Jerng UM, Kwon OJ, Jung SY, Lee JY, Yoon SW, Shin WC, Byun JI, Lee JH
2019 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Acupuncture therapy is an effective and safe treatment for chronic pain-related insomnia.
In our current study, we pooled the data from nine studies involving 944 patients. Our pooled analysis indicated that acupuncture treatment was significantly better than drugs group in improving effective rate and cure rate and in debasing PSQI score and VAS score. In addition, compared with sham acupuncture, manual acupuncture treatment has an advantage in improving the effective rate and reducing the PSQI score, but the two groups have no statistical significance in improving the cure rate. In this meta-analysis, only four studies reported relevant adverse events. The combined data showed no significant difference in adverse reactions between acupuncture group and control group. Therefore, we can carefully recommend that acupuncture is as safe as control group for CPRI. In addition, adverse events were relatively mild, mainly including bruises, soreness, nausea, dizziness, and other discomforts. These adverse events can be effectively avoided by strengthening the aseptic operation specification, and improving the professional ability of doctors. Based on the findings of our included studies, we propose that acupuncture is an effective and safe therapy for patients with CPRI.
Acupuncture for Chronic Pain-Related Insomnia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Fushui Liu, Jianyu You, Qi Li, Ting Fang, Mei Chen, Nana Tang, Xiaojun Yan
2019 Frontiers in Psychiatry
Evidence indicates that acupuncture treatment may be of benefit in several neuropsychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and Alzheimer's Disease.
The pathophysiology of these disorders may be associated with glutamate dysregulation, marked by a high rate of glutamate release and elevated expression of glutamate receptors and glutamate transporters in the CNS. The ability of acupuncture stimulation to modulate glutamate receptor and EAAT expression suggests that the treatment effects of acupuncture are underpinned by its intervention in the dysregulated glutamate system. Further preclinical and clinical studies are needed to clarify the possible mechanisms of acupuncture in these neuropsychiatric disorders and to establish protocols for treatment guidelines.
The Effects of Acupuncture on Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in Depression, Anxiety, Schizophrenia, and Alzheimer's Disease: A Review of the Literature Tu CH, MacDonald I, Chen YH
2019 Frontiers in Psychiatry
Evidence indicates that acupuncture treatment may be of benefit in several neuropsychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and Alzheimer's Disease.
The pathophysiology of these disorders may be associated with glutamate dysregulation, marked by a high rate of glutamate release and elevated expression of glutamate receptors and glutamate transporters in the CNS. The ability of acupuncture stimulation to modulate glutamate receptor and EAAT expression suggests that the treatment effects of acupuncture are underpinned by its intervention in the dysregulated glutamate system. Further preclinical and clinical studies are needed to clarify the possible mechanisms of acupuncture in these neuropsychiatric disorders and to establish protocols for treatment guidelines.
The Effects of Acupuncture on Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in Depression, Anxiety, Schizophrenia, and Alzheimer's Disease: A Review of the Literature Tu CH, MacDonald I, Chen YH
2019 Frontiers in Psychiatry
Evidence indicates that acupuncture treatment may be of benefit in several neuropsychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and Alzheimer's Disease.
The pathophysiology of these disorders may be associated with glutamate dysregulation, marked by a high rate of glutamate release and elevated expression of glutamate receptors and glutamate transporters in the CNS. The ability of acupuncture stimulation to modulate glutamate receptor and EAAT expression suggests that the treatment effects of acupuncture are underpinned by its intervention in the dysregulated glutamate system. Further preclinical and clinical studies are needed to clarify the possible mechanisms of acupuncture in these neuropsychiatric disorders and to establish protocols for treatment guidelines.
The Effects of Acupuncture on Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in Depression, Anxiety, Schizophrenia, and Alzheimer's Disease: A Review of the Literature Tu CH, MacDonald I, Chen YH
2019 Current Medical Science
Acupuncture yielded positive results for Alzheimer's Disease as determined via clinical efficacy rate, Mini-Mental State Examination score, Ability of Daily Living Scale score and Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognition score.
Eight databases were searched for articles published up to and including July 2017, and 13 studies fulfilling the inclusion criteria were identified. The main outcomes assessed were clinical efficacy rate, Mini-Mental State Examination score, Ability of Daily Living Scale score, Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognition score, Hasegawa’s Dementia Scale (HDS) score, and adverse events. The methodological quality of the articles was assessed using Cochrane’s risk of bias. All the studies compared the efficacy of acupuncture with that of medication, and were published in Chinese journals. Meta-analysis revealed that acupuncture yielded positive results as determined via all the indexes scored except the HDS. Only one of the studies reported adverse events associated with acupuncture and medication. The rate of adverse events in the medication group was 13%. In most of the studies assessed in the current meta-analysis, acupuncture alone was better than conventional western medicines for the treatment of AD.
Effectiveness of Acupuncture for Alzheimer's Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Huang, Q., Luo, D., Chen, L. et al.
2019 Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica
Acupuncture during IVF treatment can possibly lower anxiety at the time of embryo transfer but seems to have no long-term impact on women's quality of life.
A multicenter randomised controlled trial was conducted recruiting women between 18 to 42 years, who were already undergoing a fresh IVF cycle and not using acupuncture. The experiment ran between June 2011 and October 2015 in Australia and New Zealand. Random assignments placed participants in either the acupuncture group or a control group which received sham acupuncture. Three treatments were administered in total - the first between the 6th and 8th day of ovarian stimulation, and the other two on the day of the embryo transfer.
The results of the study highlighted that participants who received acupuncture reported experiencing significantly less anxiety following the embryo transfer. However, no discernible difference was found between the groups in terms of quality of life following the embryo transfer. The apparent benefit of acupuncture on the general health of participants was not sustained 14 weeks after the trial, which indicates that acupuncture might not have a long-term impact on a woman's emotional well-being following an IVF cycle.
The effects of acupuncture on the secondary outcomes of anxiety and quality of life for women undergoing IVF: A randomized controlled trial Smith CA, de Lacey S, Chapman M, Ratcliffe J, Norman RJ, Johnson NP, Fahey P
2019 Frontiers in Neuroscience
Gan Mai Da Zao decoction has shown comparable anxiolytic effects to Diazepam and Buspirone in mice, possibly regulated by serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors.
The mice were given the Gan-Mai-Da-Zao (GMDZ) decoction orally at different concentrations for a week, with Diazepam and Buspirone serving as positive controls. Anxiety-level testing was conducted using a combination of the elevated plus-maze, light/dark box, marble burying, open field, and rota-rod tests, providing a comprehensive assessment of the decoction's effects on mice.
Furthermore, the anxiolytic effects that GMDZ induced in the mice were challenged by the application of Flumazenil, a gamma-aminobutyric acid-A receptor antagonist, and WAY-100635, a serotonin-1A receptor antagonist. They found that the effects were successfully inhibited, indicating that the mechanism of action of GMDZ could be linked to both the serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors in the nervous system, thereby reducing anxiety-like behavior in mice.
GABA and 5-HT Systems Are Involved in the Anxiolytic Effect of Gan-Mai-Da-Zao Decoction Chen HS, Gu LJ, Yang YX, Guo JY
2018 Medicine
Acupuncture might have effect in decreasing the number of micturition episodes, incontinence episodes, and nocturia episodes.
Overactive bladder is stated as the occurrence of urinary urgency which will cause negative impacts and decrease patients’ health-related quality of life. The aim of this systematic review is to assess the efficiency and safety of acupuncture for adults with overactive bladder (OAB) comparing with sham-acupuncture, drugs, and acupuncture plus drugs.
Acupuncture might have effect in decreasing the number of micturition episodes, incontinence episodes, and nocturia episodes. However, the evidence is insufficient to show the effect using acupuncture alone or the additional effect to drugs in treating OAB.
Acupuncture for adults with overactive bladder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials Zhao Y, Zhou J, Mo Q, Wang Y, Yu J, Liu Z.
2018 Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine
Gan Mai Da Zao Tang, a traditional herbal formula, produced substantial antidepressant-like effects in rats by regulating monoamine neurotransmitters.
The researchers studied the antidepressant effects of Gan-Mai-Da-Zao-Tang and its constituent ingredients in rats subjected to the forced swim test. 72 male Nerl: Wistar rats aged 8 weeks were divided into groups receiving either a control solution, licorice, wheat, jujube, Gan-Mai-Da-Zao-Tang in a specific ratio, or Prozac. These substances were administered orally for 21 days. On the final day, the forced swimming test was performed which initially involved a pretest lasting 15 minutes followed by a 5 minute real test. Following this, the rats were euthanized and their brain tissues were collected for analysis of monoamine concentrations.
Discussion on the results revealed that the Gan-Mai-Da-Zao-Tang group exhibited significantly reduced immobility time and certain monoamine turnover rates, and showed an increase in concentration of some neurotransmitters in the brain tissues compared to the control group. This indicates a potent antidepressant-like effect by modulating these monoamines concentrations. In contrast, the licorice, wheat, and jujube groups didn't display significant differences when compared with the control group. Prozac, the positive control, resulted in significant reductions in body weight and appetite.
Antidepressant-like effects of Gan-Mai-Dazao-Tang via monoamine regulatory pathways on forced swimming test in rats Huang HL, Lim SL, Lu KH, Sheen LY
2018 Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences
Saffron possesses major bioactive compounds such as safranal, crocin, and picrocrocin that are hypothesized to be integral to its antidepressant effects.
In this research, a chemical analysis was undertaken on the saffron plant, a perennial herb native to various mountainous regions, ranging from Asia Minor to India. During this in-depth analysis, the researchers identified and elucidated almost 150 volatile and nonvolatile compounds from the plant. A key focus of the analysis was the three major bioactive compounds - safranal, crocin, and picrocrocin, believed to be the primary factors behind saffron's aroma and bitter taste.
On the subject of the findings, it was concluded that these major bioactive compounds are likely playing a pivotal role in the medicinal potential of the saffron plant. Specifically, the plant's well-documented antidepressant properties could largely be attributed to these compounds. The study also focused on the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of the plant, indicating that saffron could have efficacious and safe potential for use. It was inferred that this potential mainly pertains to its antidepressant effects, spurring increased interest in further exploration of its assorted bioactive compounds.
Saffron (Crocus sativus L.): As an antidepressant Siddiqui MJ, Saleh MSM, Basharuddin SNBB, Zamri SHB, Mohd Najib MH, Che Ibrahim MZ, binti Mohd Noor NA, Binti Mazha HN, Mohd Hassan N, Khatib A
2017 Journal of Physics Conference Series
Acupuncture treatment effectively improved the quality of sleep and the quality of life for chronic hemodialysis patients.
Twenty-eight hemodialysis patients suffering from insomnia were divided randomly into two groups, an acupuncture group (n = 15) who received acupuncture treatment at the points HT7 Shenmen, PC6 Neiguan, GV20 Baihui, and EX-HN1 Sishenchong, anda control group (n = 13) who underwent a sham procedure in which a needle was inserted into an elastic bandage at the same points. The acupuncture treatment was done during hemodialysis twice a week for five weeks. PSQI scores and the WHOQOL-BREF were assessed before treatment, after the fifth treatment, and at the end of the treatment. Significant differences were found in the PSQI score and in the WHOQOL-BREF between the acupuncture group and the control group by the end of the period of treatment. Acupuncture treatment effectively improved the quality of sleep and the quality of life for these chronic hemodialysis patients.
The effect of acupuncture treatment for insomnia in chronic hemodialysis patients J A Widjaja, C Simadibrata, A Srilestari, M B H Marbun
2017 Sleep and Biological Rhythms
Kiwifruit consumption before bedtime significantly improves sleep quality and daytime function in individuals with chronic insomnia in comparison to pear consumption.
In the methodology of this study, participants with chronic insomnia symptoms were randomly assigned to consume either 130g of kiwi or pear an hour prior to bedtime daily for a period of 4 weeks. This followed a baseline assessment period of one week. Various outcome measures such as sleep diaries, actigraphy, and several questionnaires were used to evaluate the effects of this dietary change.
The results showed a distinct improvement in sleep quality and daytime functionality in participants who consumed kiwi, as reported in the sleep diaries. However, the objective measures such as actigraphy and certain questionnaires did not show any significant changes. Hence, the research indicates that kiwi might have properties that enhance sleep, especially in people dealing with chronic insomnia.
The effects of kiwi fruit consumption in students with chronic insomnia symptoms: a randomized controlled trial Nødtvedt O, Hansen AL, Bjorvatn B, Pallesen S
2017 Mindfulness
iRest Yoga Nidra combined with acupuncture significantly improves psychological health in veterans compared to using acupuncture alone.
The study employed iRest Yoga Nidra, a mindfulness approach that promotes relaxation and focused attention, along with acupuncture. Initially developed for military use, iRest was combined with acupuncture in this exploratory study to determine its effectiveness. Specifically, this was tested on veterans with a view to improving their psychological health. Throughout the study, the participants were exposed to principles such as non-judgment and observation of opposing feelings and emotions, along with the inclusion of these principles into their everyday life.
The analysis of results showed that the combined therapy using iRest and acupuncture had a marked effect on psychological health. There were significant improvements in areas such as depression, psychological symptom severity, depression or tension as a result of pain, and the emotional interference with activities of daily life. Conversely, the group that had only undergone acupuncture treatment showed no significant benefits in these areas. Also significant was that the comfort shown by the treatment group was a moderate to high degree in contrast to the low comfort experienced by the group receiving only acupuncture. The overall treatment condition demonstrated considerable changes, with veterans reporting substantive decreases in the levels of mild, moderate, and severe depression. Additionally, it was indicated that the benefits of the combined treatment did not differ across factors such as age, gender, or race.
The Effect of Mindfulness and Acupuncture on Psychological Health in Veterans: an Exploratory Study Wheeler MS, Glass CR, Arnkoff DB, Sullivan P, Hull A
2015 Explore: The Journal of Science & Healing
Acupuncture seems to be an effective add-on treatment in patients with depression and, to a lesser degree, in patients with schizophrenia.
The overall clinical results on using acupuncture to treat depression are promising, but only limited evidence for its effectiveness in treating schizophrenia was found. Acupuncture improves the quality of life, particularly that of sleep, in psychiatric patients. Brain research has revealed that acupuncture has a modulating and normalizing effect on the limbic–paralimbic–neocortical network (LPNN), including the default mode network. Because the LPNN is related to sleep and emotions, this might explain the improved qualities of life and sleep after acupuncture.
Schizophrenia and Depression: A systematic Review of the Effectiveness and the Working Mechanisms Behind Acupuncture Bosch P, van den Noort M, Staudte H, Lim S.
2015 Sleep Medicine
Chinese herbal medicine was superior to placebo and benzodiazepine drugs and was superior to benzodiazepines and psychotherapy alone as an adjunct therapy in terms of subjective sleep quality and quantity and safety.
In this study, we systematically reviewed 79 RCTs investigating a variety of Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) treatments for participants with insomnia. We also performed meta-analyses to estimate the efficacy of CHM on subjective sleep quality assessed by validated instruments, patient-rated sleep parameters, clinician-reported severity, and PSG results, as well as to determine the safety of CHM.
Overall, this systematic review and meta-analysis showed that CHM was superior to placebo and benzodiazepine drugs (BZDs) when used as a monotherapy and was superior to BZDs and psychotherapy alone as an adjunct therapy in terms of subjective sleep quality and quantity and safety. CHM was not associated with more benefit than non-BZDs, although the risks were less. These results suggest that CHM could be a promising alternative therapy with a good benefit–risk ratio.
Updated clinical evidence of Chinese herbal medicine for insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials Xiaojia Ni, Johannah Linda Shergis, Xinfeng Guo, Anthony Lin Zhang, Yan Li, Chuanjian Lu, Charlie Changli Xue
2015 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
TCM pattern-based treatments for depression frequently use Xiao Yao and Chai Hu Shu Gan decoctions, with Bai Shao and Chai Hu herbs common across different TCM patterns.
The methodology incorporated a systematic review of randomized controlled trials from both Chinese and English literatures regarding traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) pattern-based treatments for depression. This encompassed a total of 61 studies and 2504 subjects across 27 TCM patterns. Due to varied TCM patterns among participants, the analysis focused on the four most prevalent ones: liver qi depression, liver depression and spleen deficiency, dual deficiency of the heart and spleen as well as liver depression and qi stagnation.
In the discussion of results, it was found that Xiaoyao decoction was most frequently used for the treatment of liver qi depression and liver depression with spleen deficiency, whereas Chaihu Shugan decoction was typically used for liver depression and qi stagnation. Commonly used herbs regardless of the prescribed Chinese herbal formulas included Bai Shao and Chai Hu. Typically, the individual studies did not provide an underlying rationale for herb selection, limiting the conclusions one could draw regarding the efficacy of certain herbal formulas and the response of specific TCM patterns to these treatments.
Prescription of Chinese Herbal Medicine in Pattern-Based Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment for Depression: A Systematic Review Yeung WF, Chung KF, Ng KY, Yu YM, Zhang SP, Ng BFL, Ziea ETC
2015 The FASEB Journal
Serotonin function, influenced by vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, plays a critical role in neuropsychiatric disorders and certain behavioral functions.
The paper synthesizes prior research into serotonin's role in managing various brain functions and behaviours, and how its dysfunction is commonly seen in conditions like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and impulsive behavior. The researchers then put forward potential mechanisms showing the influence of vitamin D and the marine omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, on serotonin synthesis, release, and function in the brain. Serotonin in the brain is synthesized from tryptophan by tryptophan hydroxylase 2, a process that is activated by a vitamin D hormone.
Possible mechanisms proposed include eicosapentaenoic acid increasing serotonin release from presynaptic neurons by lowering E2 series prostaglandins, and docosahexaenoic acid affecting serotonin receptor action by increasing cell membrane fluidity in postsynaptic neurons. The study posits that suboptimal levels of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, in combination with genetic factors at key developmental stages, could lead to dysfunctional serotonin activation and function – a possible underlying mechanism behind neuropsychiatric disorders and depression. The paper suggests that optimizing vitamin D and marine omega-3 fatty acid intake could potentially curtail and modulate the severity of brain dysfunction.
Vitamin D and the omegaâ€3 fatty acids control serotonin synthesis and action, part 2: relevance for ADHD, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and impulsive behavior Patrick RP, Ames BN
2015 The FASEB Journal
Serotonin function, influenced by vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, plays a critical role in neuropsychiatric disorders and certain behavioral functions.
The paper synthesizes prior research into serotonin's role in managing various brain functions and behaviours, and how its dysfunction is commonly seen in conditions like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and impulsive behavior. The researchers then put forward potential mechanisms showing the influence of vitamin D and the marine omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, on serotonin synthesis, release, and function in the brain. Serotonin in the brain is synthesized from tryptophan by tryptophan hydroxylase 2, a process that is activated by a vitamin D hormone.
Possible mechanisms proposed include eicosapentaenoic acid increasing serotonin release from presynaptic neurons by lowering E2 series prostaglandins, and docosahexaenoic acid affecting serotonin receptor action by increasing cell membrane fluidity in postsynaptic neurons. The study posits that suboptimal levels of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, in combination with genetic factors at key developmental stages, could lead to dysfunctional serotonin activation and function – a possible underlying mechanism behind neuropsychiatric disorders and depression. The paper suggests that optimizing vitamin D and marine omega-3 fatty acid intake could potentially curtail and modulate the severity of brain dysfunction.
Vitamin D and the omegaâ€3 fatty acids control serotonin synthesis and action, part 2: relevance for ADHD, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and impulsive behavior Patrick RP, Ames BN
2015 The FASEB Journal
Serotonin function, influenced by vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, plays a critical role in neuropsychiatric disorders and certain behavioral functions.
The paper synthesizes prior research into serotonin's role in managing various brain functions and behaviours, and how its dysfunction is commonly seen in conditions like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and impulsive behavior. The researchers then put forward potential mechanisms showing the influence of vitamin D and the marine omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, on serotonin synthesis, release, and function in the brain. Serotonin in the brain is synthesized from tryptophan by tryptophan hydroxylase 2, a process that is activated by a vitamin D hormone.
Possible mechanisms proposed include eicosapentaenoic acid increasing serotonin release from presynaptic neurons by lowering E2 series prostaglandins, and docosahexaenoic acid affecting serotonin receptor action by increasing cell membrane fluidity in postsynaptic neurons. The study posits that suboptimal levels of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, in combination with genetic factors at key developmental stages, could lead to dysfunctional serotonin activation and function – a possible underlying mechanism behind neuropsychiatric disorders and depression. The paper suggests that optimizing vitamin D and marine omega-3 fatty acid intake could potentially curtail and modulate the severity of brain dysfunction.
Vitamin D and the omegaâ€3 fatty acids control serotonin synthesis and action, part 2: relevance for ADHD, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and impulsive behavior Patrick RP, Ames BN
2013 International Review of Neurobiology
The clinical efficacy of acupuncture appeared to be supported by evidence obtained from basic neuroendocrinological studies.
A number of studies have demonstrated that acupuncture may modulate a wide range of neuroendocrinological factors following stimulation of acupoints. Evidence has suggested that the clinical efficacy of acupuncture in treatment of insomnia is potentially mediated by a variety of neurotransmitters including norepinephrine, melatonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and β-endorphin. However, due to the complexity, these findings are far from conclusive. More research is necessary. More rigors methodology and integrated approach to evaluate both clinical and basic research evidence are required for future studies.
Acupuncture for the treatment of insomnia Kaicun Zhao
2013 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Evidence of effectiveness of acupuncture for PTSD is encouraging but not cogent. Acupuncture may be a relatively safe alternative for PTSD in contrast to SSRI, if long-term therapy is needed for treatment.
This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective clinical trials on the effectiveness of acupuncture for treatment of PTSD. Only 4 RCTs and 2 UCTs met the inclusion criteria for this review. Our main finding of this review is that acupuncture is effective for PTSD based on one high-quality RCT and a meta-analysis.
Acupuncture has positive effects in PTSD patients, although the evidence is still lacking as to its true efficacy for this condition.
Acupuncture for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials and Prospective Clinical Trials Young-Dae Kim, In Heo, Byung-Cheul Shin, Cindy Crawford, Hyung-Won Kang, Jung-Hwa Lim,
2011 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
Acupuncture might result in improvement in some outcomes in children with autism spectrum disorders.
When needle acupuncture plus conventional treatment was compared to sham acupuncture plus conventional treatment, the intervention seemed to result in better language comprehension, cognition, selfâ€care, social function and a higher likelihood of greater than or equal to 25% improvement in global function.
Compared to conventional treatment alone, needle acupuncture plus conventional treatment might result in an overall improvement in autistic features, speech, cognition, global functioning, selfâ€care, sensory functioning, imitation, repetitive behaviour, and physical health.
Compared to conventional treatment alone, acupressure plus conventional treatment might result in improvement in overall global functioning, communication attitude, nonâ€verbal communication and matching, and language and social interaction.
Acupuncture for autism spectrum disorders (ASD) Cheuk DKL, Wong V, Chen WX
2010 Journal of Medicinal Food
Tart cherry juice blend yielded modest improvements in sleep for older adults with insomnia, exhibiting effects similar to or better than natural products like valerian and melatonin.
In the pilot study, 15 older adults who were suffering from chronic insomnia but were otherwise healthy participated in a randomized, double-blind, crossover design. The study lasted for 6 weeks, with each participant receiving both the proprietary tart cherry juice blend and a placebo for 2 weeks with a 2-week washout period between the two treatments. Sleep continuity and insomnia severity were evaluated by analyzing 2-week mean values derived from daily sleep diaries and the Insomnia Severity Index respectively.
The tart cherry juice blend was found to bring significant improvements in all assessed sleep variables before and after treatment. These improvements were particularly noticed in reducing insomnia severity, specifically the minutes awake after sleep onset, compared to placebo. Sleep latency, total sleep time, or sleep efficiency didn't show any notable improvements compared to placebo. The benefits of the tart cherry juice on sleep for older adults with insomnia were in the range of effect sizes seen in studies using valerian or melatonin, which are the most commonly studied natural products for insomnia. But these effects were considerably less than evidence-based insomnia treatments such as hypnotic agents and cognitive-behavioral therapies.
Effects of a Tart Cherry Juice Beverage on the Sleep of Older Adults with Insomnia: A Pilot Study Pigeon WR, Carr M, Gorman C, Perlis ML
2009 The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine
Clinical studies have shown that acupuncture may have a beneficial effect on insomnia compared with Western medication.
Forty-six (46) randomized trials involving 3811 patients were included, and the methodological quality of trials was generally fair in terms of randomization, blinding, and intention-to-treat analysis. Meta-analyses showed a beneficial effect of acupuncture compared with no treatment and real acupressure compared with sham acupressure on total scores of Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Acupuncture was superior to medications regarding the number of patients with total sleep duration increased for >3 hours. However, there was no difference between acupuncture and medications in average sleep duration. Acupuncture plus medications showed better effect than medications alone on total sleep duration. Similarly, acupuncture plus herbs was significantly better than herbs alone on increase of sleep rates. There were no serious adverse effects with related to acupuncture treatment in the included trials.
Acupuncture for Treatment of Insomnia: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Cao H, Pan X, Li H, Liu J.
Consult with our practitioners for personalised care and advice.
Although well-conducted clinical research can help members of the public to make better-informed decisions about their healthcare, we cannot claim that any particular treatment may be effective for any individual person.
When you consult with our Chinese medicine practitioners, you'll receive personalised advice and treatment based on your symptoms and Chinese medicine diagnosis.
Scientific References
Browse our collection of scientific clinical research on acupuncture for mental health.
It includes recent and reputable papers published by peer-reviewed journals within the last 10 years.

2024, Feb
Pumpkin Seeds (Cucurbita spp.) as a Nutraceutical Used In Various Lifestyle Disorders
The Natural Products Journal
The therapeutic benefits of pumpkin seeds & the potential disease-preventing mechanisms are updated in this review article, also on the chemical make-up, nutritional value, phytochemical research, pharmacological characteristics, bioavailability, food use, & industrial applications of pumpkin.
Wal A, Singh MR, Gupta A, Rathore S, Rout RR, Wal P Full Article

2023, Apr 04
Vitamin D in Depression: A Potential Bioactive Agent to Reduce Suicide and Suicide Attempt Risk
Nutrients
Several studies have shown that deficiencies in this vitamin reduce the immunomodulation of inflammation and serotonin synthesis, two processes associated with depression and suicidal attempts. Therefore, it supports the potential benefits of vitamin D supplementation in reducing symptoms of depression and a possible indirect effect in the prevention of suicide and suicide attempts.
Somoza-Moncada MM, Turrubiates-Hernández FJ, Muñoz-Valle JF, Gutiérrez-Brito JA, DÃaz-Pérez SA, Aguayo-Arelis A, Hernández-Bello J Full Article

2023, Mar
Acupuncture as an Adjunct Treatment to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia
Sleep Medicine Clinics
The study concludes that there is growing evidence supporting the effectiveness of acupuncture in treating insomnia and comorbid conditions, and further research is needed to explore its potential as an adjunct to CBT-I.
Kutana S, Mao JJ, Garland SN Full Article

2023, Sep
Effects of Pueraria lobata root and Glycine max (L.) Merrill extracts fermented with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the depressive-like behavior in ovariectomized mice via upregulation of hippocampal BDNF
Journal of Functional Foods
Fermented P. lobata root extract (FPE), fermented G. max (L.) Merrill extract (FGE), and a mixture of the two extracts (FPE-FGE) can be used as a raw material for the development of dietary supplements for menopausal women as they increase ERβ expression and alleviate depressive-like behavior through the regulation of BDNF and neurotransmitters.
Ha J, Jang HM, Choi I Full Article

2022, Dec 12
Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for depression: A systematic review and metaâ€analysis
Research in Nursing & Health
Acupuncture, either in isolation or as an adjunct to pharmacological treatment, has clinical benefits and can be considered a safe option for managing depression.
Chen B, Wang CC, Lee KH, Xia JC, Luo Z Full Article

2022, Dec 31
Effect of Acupuncture on Physical Symptoms and Quality of Life in Treatment-Resistant Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder: a Single-Arm Longitudinal Study
Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies Medical Association of Pharmacopuncture Institute
Acupuncture may improve not only psychiatric symptoms but also physical symptoms and QoL in patients with treatment-resistant mood disorders. Further studies are required for confirmation of the preliminary data collected thus far.
Matsuura Y, Hongo S, Taniguchi H, Yasuno F, Sakai T Full Article

2022, Aug
Research progress on classical traditional chinese medicine formula xiaoyaosan in the treatment of depression
Frontiers in Pharmacology
This review highlights the current evidence supporting the use of Xiaoyaosan as an antidepressant and provides an overview of the potential mechanisms involved.
Chen J, Lei C, Li X, Wu Q, Liu C, Ma Q, Chen J. Full Article

2022, Jan 14
Can acupuncture improve sleep quality and anxiety among women during perimenopause?
Medicine
This study will provide new evidence on the effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for the treatment of insomnia, anxiety, and depression in perimenopausal women, and provide additional options for clinicians and patients to improve insomnia and anxiety.
Ping Y, Liang C, Fan X, Zhang L, Ying D, Wang Z Full Article

2022, Apr 06
Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of Xiao Yao San as a Treatment for Anxiety: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
The available evidence suggests that oral Xiaoyao San (XYS) alone or in combination with anxiolytic agents is more effective and safer than anxiolytic treatment alone when used for the treatment of anxiety disorders (AD).
Lin J, Ji Y, Si J, Wang G, Li X, Shen L Full Article

2022, Jan 31
A network pharmacology approach to predict potential targets and mechanisms of “Ramulus Cinnamomi (cassiae) – Paeonia lactiflora†herb pair in the treatment of chronic pain with comorbid anxiety and depression
Annals of Medicine
This study preliminarily predicted and verified the pharmacological and molecular mechanisms of “Gui Zhi–Shao Yao†herb pair for treating CP with comorbid AD and MD from a holistic perspective. In vivo and in vitro experiments will be required to further investigate the mechanisms.
Pan HT, Xi ZQ, Wei XQ, Wang K Full Article

2022, Aug
Screening Traditional Chinese Medicine Combination for Co-Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease and Major Depressive Disorder by Network Pharmacology
Natural Product Communications
Taken as a whole, the current study indicates a TCM combination with positive advantages in the combined treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and major depressive disorder (MDD) .
Huang Z, Fang Y, Wang X, Wang Q, Wang T Full Article

2022, Apr 15
The Role of Acupuncture in the Management of Insomnia as a Major or Residual Symptom Among Patients With Active or Previous Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Frontiers in Psychiatry
There is a low to moderate level of evidence supporting acupuncture as a safe and effective remedy alternative to or adjuvant to conventional pharmacotherapy (antidepressant and/or hypnotic) in improving insomnia and other depression symptoms among patients with active depression. Furthermore, the patients' complaint of disrupted sleep continuity is most likely to benefit from acupuncture. The benefit of acupuncture on residual insomnia associated with previous or partially remitted depression is limited. Future acupuncture studies need to consider applying optimal dosage and addressing deficiencies in trial quality.
Zhao FY, Kennedy GA, Spencer SJ, Conduit R, Zhang WJ, Fu QQ, Zheng Z Full Article

2022, Jan 19
Major Plant in Herbal Mixture Gan-Mai-Da-Zao for the Alleviation of Depression in Rat Models
Plants
The present study confirmed the antidepressant-like effects of Gan-Mai-Da-Zao (GMDZ). Additionally, licorice (Gan Cao) may play a key role in the effectiveness of GMDZ.
Li YX, Cheng KC, Hsu CT, Cheng JT, Yang TT Full Article

2022, Jul 14
Chinese Herbal Medicine for Functional Dyspepsia With Psychological Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Frontiers in Neuroscience
The current evidence shows that CHM treatment has great potential and safety in alleviating the symptoms of FD and improving the psychological disorders of anxiety and depression in patients with FD.
Luo X, Wang L, Fang S, Qing X, Jiang T, Yang Y, Su X, Wei W Full Article

2022, Jun 27
Modified Xiaochaihu Decoction Combined with Mirtazapine in the Treatment of Persistent Depression: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Frontiers in Pharmacology
Modified Xiaochaihu Decoction combined with mirtazapine effectively treats persistent depressive disorder (PDD), and its curative effect is better than that of TCM alone.
Xin Li, Xiuyu Li, Man Gong, Chaoqun Li, Jing Li, Chao Zhou, Tingting He Full Article

2022, Apr
The association study of chemical compositions and their pharmacological effects of Cyperi Rhizoma (Xiangfu), a potential traditional Chinese medicine for treating depression
Journal of Ethnopharmacology
Cyperi Rhizoma (CR) could be a significant potential herbal medicine to develop antidepressant drugs with lower side effects.
Lu J, Li W, Gao T, Wang S, Fu C, Wang S Full Article

2022, Nov 03
The Role of Kiwifruit in Supporting Psychological Well-Being: A Rapid Review of the Literature
Nutrients
Overall, preliminary evidence suggests that daily consumption of two gold kiwifruit might improve psychological well-being in adult populations.
Billows M, Kakoschke N, Zajac IT Full Article

2022, May
The effects of Lavender and Chamomile essential oil inhalation aromatherapy on depression, anxiety and stress in older community-dwelling people: A randomized controlled trial
Explore: The Journal of Science & Healing
Inhalation aromatherapy with both lavender and chamomile essential oils resulted in a statistically significant improvement in depression, anxiety, and stress levels in community-dwelling older adults.
Ebrahimi H, Mardani A, Basirinezhad MH, Hamidzadeh A, Eskandari F Full Article

2022, Dec 27
A Chinese Classical Prescription Chaihu Shugan Powder in Treatment of Post-Stroke Depression: An Overview
Medicina
CHSG shows promising clinical efficacy and mechanisms of action in treating PSD, providing a potential alternative to traditional antidepressant medications.
Gao Z, Wang Y, Yu H Full Article

2022, May 05
Evidence and Characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Coronary Heart Disease Patients With Anxiety or Depression: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
Frontiers in Pharmacology
Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) exhibited an obvious efficacy in treating coronary heart disease (CHD) patients with anxiety or depression, especially for improving the symptom of angina pectoris. The most active compounds of CHM could simultaneously act on the pathological targets of CHD, anxiety, and depression. Multiple effective components and multiple targets were the advantages of CHM compared with WM.
Wang B, Teng Y, Li Y, Lai S, Wu Y, Chen S, Li T, Han X, Zhou H, Wang Y, Lu Z, Li H, Ding Y, Ma L, Zhao M, Wang X Full Article

2021, Jan 30
Effectiveness of acupuncture on anxiety disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Annals of General Psychiatry International Society of Neurobiology and Psychopharmacology
The study suggest that acupuncture therapy showed beneficial effects in reducing anxiety in patients with anxiety disorder. It indicated that acupuncture is more effective than western medicine. It also further suggests that acupuncture works better in earlier stages.
Yang, Xy., Yang, Nb., Huang, Ff. et al. Full Article

2021, May 24
Efficacy and Safety of Scalp Acupuncture for Insomnia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Scalp acupuncture is effective and safe in the treatment of insomnia, which is worthy of clinical application. However, due to the limited number of included literature, the methodology of some studies is slightly low and the quality of literature is slightly poor. In the future, we need to design rigorous, large sample, multiple center randomized controlled study to further verify the conclusion of this study.
Fu-gui Liu, Ai-hua Tan, Chao-qun Peng, Yun-xia Tan, Ming-chao Yao Full Article

2021, May
Impact of saffron (Crocus Sativus Linn) supplementation and resistance training on markers implicated in depression and happiness levels in untrained young males
Physiology & Behavior
Untrained young male participants were randomly assigned to either RT + saffron supplement (RS) or RT + placebo (RP) groups. After 6 weeks of supervised RT, participants in the RS group showed significant increases in concentrations of Anandamide (AEA), 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), dopamine, and β-endorphin, along with significant improvements in serotonin levels and happiness levels. Muscular endurance also increased in both groups, with greater changes observed in the RS group. The study suggests that the combination of saffron supplementation and resistance training may have positive effects on both markers related to depression and happiness levels in untrained young males.
Moghadam BH, Bagheri R, Roozbeh B, Ashtary-Larky D, Gaeini AA, Dutheil F, Wong A Full Article

2021, Jun
Dietary prospects of coconut oil for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD): A review of recent evidences
Trends in Food Science & Technology
The study concludes that coconut oil has significant therapeutic value in the prevention or treatment of AD, based on its multi-pronged biochemical effects.
Ramesh SV, Krishnan V, Praveen S, Hebbar KB Full Article

2021, Nov
Effects of Acupuncture and Acupressure on Burnout in Health Care Workers: A Randomized Trial
Journal of Trauma Nursing
Auricular seed acupressure was found to be associated with a reduction in burnout and secondary traumatic stress in health care workers, leading to improved professional quality of life and caring ability.
Afrasiabi J, McCarty R, Hayakawa J, Barrows J, Lee K, Plouffe N, Schomberg J Full Article

2020, Jan
Placebo effect of acupuncture on insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Annals of Palliative Medicine
Compared to the sham groups, acupuncture significantly decreased the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) score. In addition, a significant difference was detected in the change of Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) scores between acupuncture and sham acupuncture. The authors concluded that acupuncture treatment of insomnia is efficacious, not because of its placebo effect.
Liu C, Xi H, Wu W, Wang X, Qin S, Zhao Y, Zheng S, Wan Q, Xu L. Full Article

2020, Dec
Long-Term Beneficial Effects of Acupuncture with Reduced Risk of Depression Development Following Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment
The systematic review and meta-analysis also concluded that the therapeutic efficacy of acupuncture is highly effective alone and combined with antidepressant medication.
Liao CC, Lin CL, Liao KR, Li JM Full Article

2020, Jun 25
Effect of Acupuncture on Chronic Pain with Depression: A Systematic Review
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Acupuncture has a promising application prospect due to its unique advantages for the treatment of chronic pain with depression comorbidity, which can be used in patients suffering from some certain chronic pain with depression comorbidity with poorer response to the conventional medication or suffering from serious side effects. High-quality RCTs are needed to support the current clinical application of acupuncture for the treatment of chronic pain with depression comorbidity and to broaden the clinical application.
Yan B, Zhu S, Wang Y, Da G, Tian G Full Article

2020, Nov 27
Acupuncture for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: An Overview of Systematic Reviews
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience
This overview suggests that acupuncture is a promising complementary treatment for Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Huang J, Shen M, Qin X, Wu M, Liang S, Huang Y Full Article

2020, Nov 26
Effects of Matcha Green Tea Powder on Cognitive Functions of Community-Dwelling Elderly Individuals
Nutrients
The study found that daily supplementation of Matcha Green Tea Powder has protective effects against cognitive decline in community-dwelling elderly women.
Sakurai K, Shen C, Ezaki Y, Inamura N, Fukushima Y, Masuoka N, Hisatsune T Full Article

2020, Jan
Comparative Effectiveness of Cheonwangbosimdan (Tian Wang Bu Xin Dan) Versus Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia in Cancer Patients: A Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Parallel-Group, Pilot Trial
Integrative Cancer Therapies
There is no difference between treatment and control groups, but both groups showed tendency to alleviate cancer insomnia symptoms. However, treatment group score was highly lowered than control group score. The study can contribute to more attentive care for insomnia in cancer patients.
Moon SY, Jerng UM, Kwon OJ, Jung SY, Lee JY, Yoon SW, Shin WC, Byun JI, Lee JH Full Article

2019, Jun 24
Acupuncture for Chronic Pain-Related Insomnia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Acupuncture therapy is an effective and safe treatment for CPRI, and this treatment can be recommended for the management of patients with CPRI. Due to the low quality and small sample size of the included studies, more rigorously designed RCTs with high quality and large sample size are recommended in future.
Fushui Liu, Jianyu You, Qi Li, Ting Fang, Mei Chen, Nana Tang, Xiaojun Yan Full Article

2019, Feb 12
The Effects of Acupuncture on Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in Depression, Anxiety, Schizophrenia, and Alzheimer's Disease: A Review of the Literature
Frontiers in Psychiatry
We conclude that the treatment effects of acupuncture may be underpinned by its intervention in the dysregulated glutamate system. Further preclinical and clinical studies are needed to clarify the possible mechanisms of acupuncture in these neuropsychiatric disorders and to establish protocols for treatment guidelines.
Tu CH, MacDonald I, Chen YH Full Article

2019, Jun 17
Effectiveness of Acupuncture for Alzheimer's Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Current Medical Science Huazhong University of Science and Technology
In most of the studies assessed in the current meta-analysis, acupuncture alone was better than conventional western medicines for the treatment of AD.
Huang, Q., Luo, D., Chen, L. et al. Full Article

2019, Jan 20
The effects of acupuncture on the secondary outcomes of anxiety and quality of life for women undergoing IVF: A randomized controlled trial
Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Acupuncture may reduce anxiety at embryo transfer. Quality of life did not differ between the groups. Women experience reduced emotional well-being 3 months following the IVF cycle, highlighting ongoing unmet psycho-social needs.
Smith CA, de Lacey S, Chapman M, Ratcliffe J, Norman RJ, Johnson NP, Fahey P Full Article

2019, Jan 22
GABA and 5-HT Systems Are Involved in the Anxiolytic Effect of Gan-Mai-Da-Zao Decoction
Frontiers in Neuroscience
The present data show that GMDZ decoction possesses strong anxiolytic-like effects in the EPM, LDB, and OF tests but did not alters locomotor activity and motor coordination. The antagonism experiments suggest that the mode of action for GMDZ is via the GABAergic and serotonergic systems.
Chen HS, Gu LJ, Yang YX, Guo JY Full Article

2018, Feb 23
Acupuncture for adults with overactive bladder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Medicine
The combined results showed that electroacupuncture (EA) may be more effective than sham electroacupuncture (sham EA) in improving the 24-hour nocturia episodes and EA may enhance tolterodine for relieving voiding symptoms and enhancing patients’ quality of life. Acupuncture might have effect in decreasing the number of micturition episodes, incontinence episodes, and nocturia episodes.
Zhao Y, Zhou J, Mo Q, Wang Y, Yu J, Liu Z. Full Article

2018, Jan
Antidepressant-like effects of Gan-Mai-Dazao-Tang via monoamine regulatory pathways on forced swimming test in rats
Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan
In conclusion, the antidepressant-like effects of Gan-Mai-Da-Zao-Tang (LWJ) might be mediated by the regulation of monoamine neurotransmitters.
Huang HL, Lim SL, Lu KH, Sheen LY Full Article

2018, Jan
Saffron (Crocus sativus L.): As an antidepressant
Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences
The study concludes that saffron has potential as an antidepressant and contains various bioactive compounds such as safranal, crocin, and picrocrocin.
Siddiqui MJ, Saleh MSM, Basharuddin SNBB, Zamri SHB, Mohd Najib MH, Che Ibrahim MZ, binti Mohd Noor NA, Binti Mazha HN, Mohd Hassan N, Khatib A Full Article

2017, Aug 30
The effect of acupuncture treatment for insomnia in chronic hemodialysis patients
Journal of Physics Conference Series
Acupuncture treatment effectively improved the quality of sleep and the quality of life for these chronic hemodialysis patients.
J A Widjaja, C Simadibrata, A Srilestari, M B H Marbun Full Article

2017, Mar 06
The effects of kiwi fruit consumption in students with chronic insomnia symptoms: a randomized controlled trial
Sleep and Biological Rhythms
Results showed that on a total of two out of 12 outcome variables (sleep quality and daytime functioning as reported using sleep diary), there was a statistically significant group × time interaction effect favoring the kiwi condition compared to pear. Although there were no such effects using objective measures, the results suggest that kiwi may possess some sleep improving properties.
Nødtvedt O, Hansen AL, Bjorvatn B, Pallesen S Full Article

2017, Aug 29
The Effect of Mindfulness and Acupuncture on Psychological Health in Veterans: an Exploratory Study
Mindfulness
The combined treatment of iRest plus acupuncture resulted in significant psychological benefits for Veterans, particularly in reducing depression, psychological symptom severity, and emotional interference with life activities, with clinically meaningful changes noted. Additionally, the combined treatment was equally beneficial across different demographic factors such as age, gender, and race.
Wheeler MS, Glass CR, Arnkoff DB, Sullivan P, Hull A Full Article

2015, Jul
Schizophrenia and Depression: A systematic Review of the Effectiveness and the Working Mechanisms Behind Acupuncture
Explore: The Journal of Science & Healing
From the evidence found in this study, acupuncture seems to be an effective add-on treatment in patients with depression and, to a lesser degree, in patients with schizophrenia, but large well-designed studies are needed to confirm that evidence.
Bosch P, van den Noort M, Staudte H, Lim S. Full Article

2015, Dec
Updated clinical evidence of Chinese herbal medicine for insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Sleep Medicine
Overall, oral CHM used as a monotherapy or as an adjunct to conventional therapies appears safe, and it may improve subjective sleep in people with insomnia. However, the typical effect of CHM for insomnia cannot be determined due to heterogeneity. Further study focusing on individual CHM formula for insomnia is needed. The development of a comparable placebo is also needed to improve the successful blinding in RCTs.
Xiaojia Ni, Johannah Linda Shergis, Xinfeng Guo, Anthony Lin Zhang, Yan Li, Chuanjian Lu, Charlie Changli Xue Full Article

2015, Jan
Prescription of Chinese Herbal Medicine in Pattern-Based Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment for Depression: A Systematic Review
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
We found that Xiaoyao decoction was the most frequently used herbal formula for the treatment of liver qi depression and liver depression with spleen deficiency, while Chaihu Shugan decoction was often used for liver depression and qi stagnation. Bai Shao (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) and Chai Hu (Bupleurum chinense DC.) were commonly used across different TCM patterns regardless of the prescribed Chinese herbal formulas. The rationale underlying herb selection was seldom provided. Due to the limited number of studies on TCM pattern-based treatment of depression and their low methodological quality, we are unable to draw any conclusion regarding which herbal formulas have higher efficacy and which TCM patterns respond better to CHM.
Yeung WF, Chung KF, Ng KY, Yu YM, Zhang SP, Ng BFL, Ziea ETC Full Article

2015, Feb 24
Vitamin D and the omegaâ€3 fatty acids control serotonin synthesis and action, part 2: relevance for ADHD, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and impulsive behavior
The FASEB Journal
We propose a model whereby insufficient levels of vitamin D, EPA, or DHA, in combination with genetic factors and at key periods during development, would lead to dysfunctional serotonin activation and function and may be one underlying mechanism that contributes to neuropsychiatric disorders and depression. This model suggests that optimizing vitamin D and marine omega-3 fatty acid intake may help prevent and modulate the severity of brain dysfunction.
Patrick RP, Ames BN Full Article

2013, Jan
Acupuncture for the treatment of insomnia
International Review of Neurobiology
A number of studies have demonstrated that acupuncture may modulate a wide range of neuroendocrinological factors following stimulation of acupoints. Evidence has suggested that the clinical efficacy of acupuncture in treatment of insomnia is potentially mediated by a variety of neurotransmitters including norepinephrine, melatonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and β-endorphin.
Kaicun Zhao Full Article

2013, Feb
Acupuncture for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials and Prospective Clinical Trials
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
This systematic review indicated the efficacy of acupuncture for PTSD patients. Patients reported to have better outcomes compared to drug therapy in particular selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI). There were less side effects for non-SSRI group and considered a safe treatment for long term therapy.
Young-Dae Kim, In Heo, Byung-Cheul Shin, Cindy Crawford, Hyung-Won Kang, Jung-Hwa Lim, Full Article

2011, Sep 07
Acupuncture for autism spectrum disorders (ASD)
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Cochrane
This review found that acupuncture might result in improvement in some outcomes in children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). However, the high heterogeneity of the result did not provide a firm conclusion.
Cheuk DKL, Wong V, Chen WX Full Article

2010, Jun
Effects of a Tart Cherry Juice Beverage on the Sleep of Older Adults with Insomnia: A Pilot Study
Journal of Medicinal Food Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition
The results of this pilot study suggest that CherryPharm, a tart cherry juice blend, has modest beneficial effects on sleep in older adults with insomnia with effect sizes equal to or exceeding those observed in studies of valerian and in some, but not all, studies of melatonin, the two most studied natural products for insomnia.
Pigeon WR, Carr M, Gorman C, Perlis ML Full Article

2009, Nov
Acupuncture for Treatment of Insomnia: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine Society for Acupuncture Research
Acupuncture appears to be effective in treatment of insomnia. Meta-analyses showed a beneficial effect of acupuncture compared with no treatment and real acupressure compared with sham acupressure on total scores of Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Acupuncture was superior to medications regarding the number of patients with total sleep duration increased for >3 hours. Acupuncture plus medications showed better effect than medications alone on total sleep duration. Similarly, acupuncture plus herbs was significantly better than herbs alone on increase of sleep rates. There were no serious adverse effects with related to acupuncture treatment in the included trials.
Cao H, Pan X, Li H, Liu J. Full Article
“It is by virtue of the twelve channels that human life exists, that disease arises, that human beings can be treated and illness cured. The twelve channels are where beginners start and masters end.” The Classic of Acupuncture
Circa 1st Century BCE